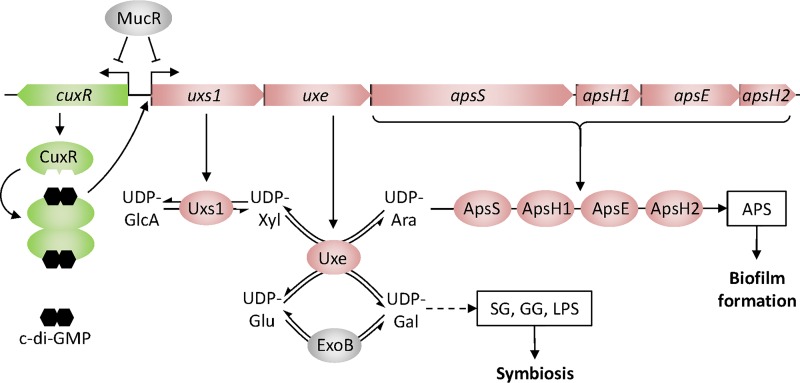
FIG 6.
Model of Uxe function in biosynthesis of cell surface polysaccharides in S. meliloti. The combined activities of UDP-xylose synthase Uxs1 and UDP-xylose 4-epimerase Uxe result in the formation of UDP-arabinose, a nucleotide-sugar precursor in the biosynthesis of an arabinose-containing polysaccharide (APS) that promotes biofilm formation. Similar to ExoB and in addition to its UDP-xylose 4-epimerase activity, Uxe catalyzes epimerization between UDP-glucose and UDP-galactose, thereby supporting biosynthesis of the symbiotically relevant polysaccharides succinoglycan (SG), galactoglucan (GG), and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Opposite transcriptional regulation of the aps operon by CuxR–c-di-GMP and MucR integrates the APS biosynthesis pathway into the global regulatory network of exopolysaccharide biosynthesis and swimming motility. UDP-GlcA, UDP-glucuronate; UDP-Xyl, UDP-xylose; UDP-Ara, UDP-arabinose; UDP-Glu, UDP-glucose; UDP-Gal, UDP-galactose.