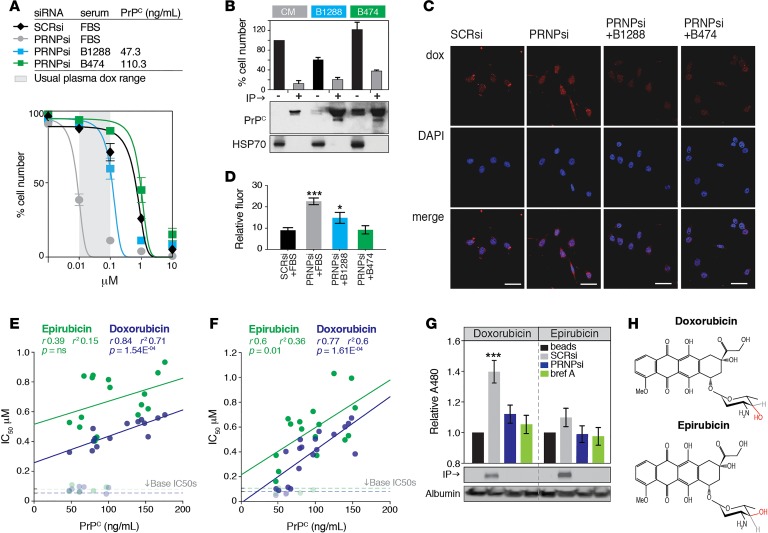
Figure 3. Effect of PrPC-positive serum and tumor tissue on doxorubicin efficacy.
(A) Comparison of doxorubicin dose-response profiles in HM.LNm5 cells supplemented with 10% FBS or 10% serum from patients B1288 or B474. For patient serum assays, cells were first depleted of endogenous PRNP using siRNA. Serum PrPC concentration was measured by ELISA. The assay was performed within a physiologically relevant range of doxorubicin concentrations (gray shading, 10–100 nM, 24–96 hours after infusion of 75 mg/m2 dose; ref. 14). (B) PRNP-depleted HM.LNm5 cells were incubated for 72 hours with conditioned medium from SCRsi-transfected HM.LNm5 (CM) cells or media from PRNP-depleted HM.LNm5 cells supplemented with 10% human serum. Parallel cultures were incubated after specific depletion of PrPC by immunoprecipitation (IP; 3F4 antibody). Western shows PrPC levels (with 1% of input blotted for HSP70 as a loading control), and the bar graph shows the effect of depleting PrPC from the media on total cell number after 72 hours growth in the presence of doxorubicin (1 μM; mean ± SEM from 3 assays). (C and D) Fluorescent imaging of doxorubicin (red) in the nuclei of PRNP-depleted HM.LNm5 cells cultured with human serum. Ten image fields were analyzed in triplicate (PRNPsi, ***P = 0.002; +B1288, *P = 0.045). Scale bar: 100 nm. (E) Correlation between patient serum PrPC concentration (determined by ELISA) and doxorubicin or epirubicin IC50 in PRNP-depleted HM.LNm5 cells. Samples were tested in duplicate. (F) Correlation between patient serum PrPC concentration and doxorubicin or epirubicin IC50 in PRNP-depleted BT549 cells. (G) Co-IP of doxorubicin or epirubicin in conditioned media of HM.LNm5 cells by PrPC using 3F4, with fluorescent readout at 480 nm compared with control IP of beads alone. Conditioned media albumin was a loading control (mean ± SEM is shown for 3 experiments; ***P = 0.005). (H) Comparison of doxorubicin and epirubicin structures, highlighting epimerization of the sugar moiety hydroxyl group.