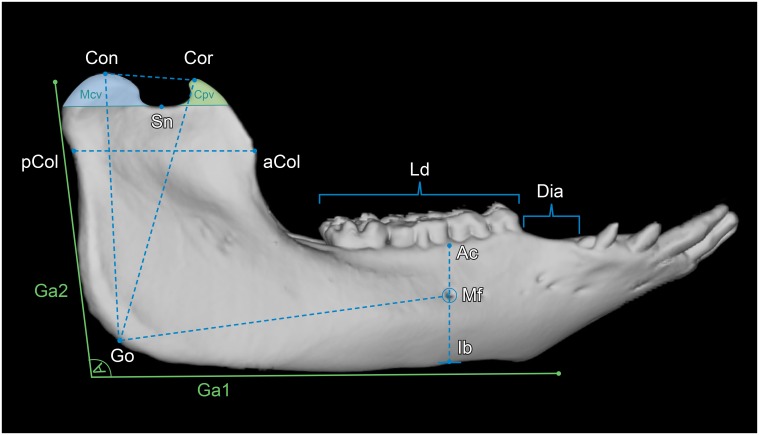
Fig 1. Lateral view of a 3D rendered mandible of a 17 months-old Göttingen Minipig with landmarks and measured parameters.
Where: Con = condylion, Cor = coronion, Sn = lowest point of the sigmoid notch, pCol = posterior point of the mandibular collum, aCol = anterior point of the mandibular collum, Ga1 = horizontal tangent alongside the inferior border of the mandibular body, Ga2 = near vertical tangent alongside the posterior border of the mandibular ramus, Ac = point on the buccal alveolar crest at the vertical level of the posterior mental foramen, Mf = posterior prominent mental foramen, Ib = most inferior point of the mandibular body at the vertical level of the posterior mental foramen, Go = gonion. The parameters measured were: Con–Go = mandibular ramus height (MRH), Cor–Go = oblique mandibular ramus height (oMRH), Dia = diastemal length (DL), Ld = premolar and molar dental arch length (DAL), Mf–Ib = mental foramen to inferior border (MIB), Mf–Ac = mental foramen to alveolar crest (MAC), Mf–Go = mental foramen to gonion (MGO), Ga1-Ga2 = gonial angle (GA), aCol–pCol = mandibular ramus length (MRL), Cor–Con = superior ramus length (SRL), Cpv = coronoid process volume (CPV), Mcv = mandibular condyle volume (MCV).