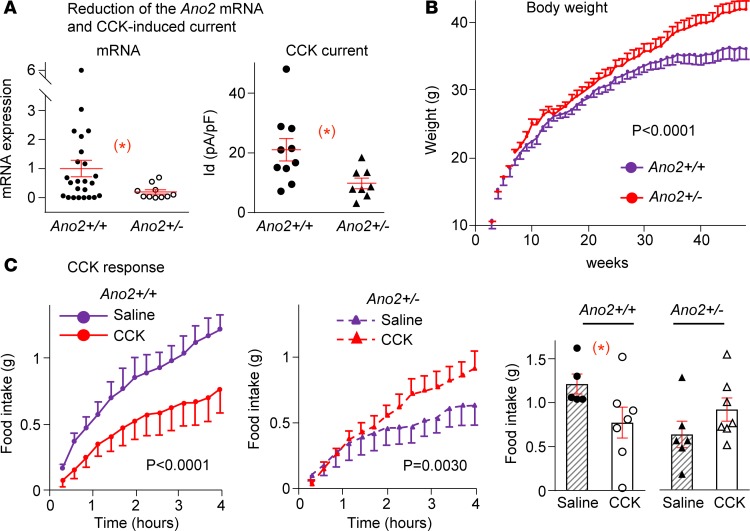
Figure 4. Weight gain and CCK-8 responses of heterozygote TMEM16B-KO mice.
(A) Conditional KO of Ano2/TMEM16B in Nav1.8Cre;Ano2fl/WT (Ano2+/–) mice leads to a significant reduction of mRNA levels in individual nodose neurons compared with littermate controls (Ano2+/+), from 1.00 ± 0.28 to 0.20 ± 0.08 (n = 24 and 10 neurons from 8 ganglia of 4 mice for each group, *P < 0.05). The CCK-induced current is significantly reduced from 21.1 ± 3.7 to 9.8 ± 1.8 pA/pF (n = 10 and 8 neurons from 6 ganglia of 3 mice for Ano2+/+ and Ano2+/– groups, respectively, *P < 0.05). Unpaired Student’s t test. (B) The Ano2+/– mice gained more weight, with their maximal body weight averaging 41.9 ± 1.3 g (n = 14) vs. 36.0 ± 1.5 g in control mice (n = 14, P < 0.0001, 2-way ANOVA). (C) CCK-8 suppresses the cumulative 4-hour food intake following fasting significantly (n = 7) compared with saline (n = 5) in Ano2+/+ (left panel, P < 0.0001) but increases food intake in Ano2+/– mice (n = 7) compared with saline (n = 6; middle panel, P = 0.0030, 2-way ANOVA). The total 4-hour food intake (bar graph) decreases with CCK from 1.21 ± 0.11 to 0.77 ± 0.18 g (*P < 0.05, unpaired Student’s t test) in Ano2+/+ and increases from 0.63 ± 0.15 to 0.91 ± 0.13 g (P > 0.05, unpaired Student’s t test) in Ano2+/– mice. Data are presented as means ± SEM; each symbol represents individual nodose neurons in A and represents individual mice in C.