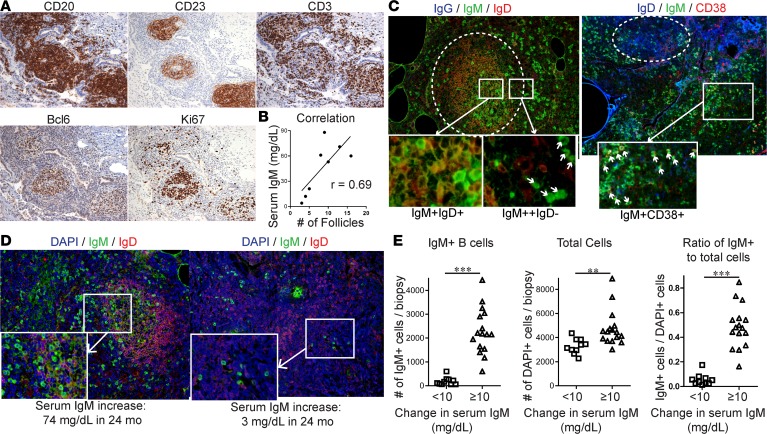
Figure 2. Serum IgM increase reflects B cell hyperplasia and local IgM production in CVID ILD.
(A) CD20+CD23+CD3+Bcl6+Ki67+ ectopic B cell follicles (serial sections from the same patient, ×200 magnification) in CVID ILD biopsies were quantified and (B) correlated with serum IgM (Spearman’s r = 0.69) in 8 patients. (C) These ectopic B cell follicles in CVID patients expressed IgM and IgD, but not IgG, and extrafollicular IgMbrightIgD–CD38+ plasmablasts were also identified (marked with white arrows). Larger images of ×200 magnification with ×1,600 and ×400 magnification insets, respectively. Data representative of those from 6 subjects. (D) Representative images showing that lung biopsies from CVID patients with greater serum IgM increase over 24 months had more IgM+ cells in the lungs. Original magnification, ×200 and ×400 (insets). (E) Quantification of IgM+ cells of lung biopsies from 13 CVID ILD patients (5 stable ILD, 8 progressive ILD) in which lung tissue was available (2 non-serial sections from each patient included) demonstrated significantly greater IgM+ B cells, total cells (DAPI+), and ratio of IgM+ cells to total cells in progressive ILD patients with serum IgM increase ≥ 10 mg/dl compared with those with stable ILD as quantified using CellProfiler software. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by Mann-Whitney test.