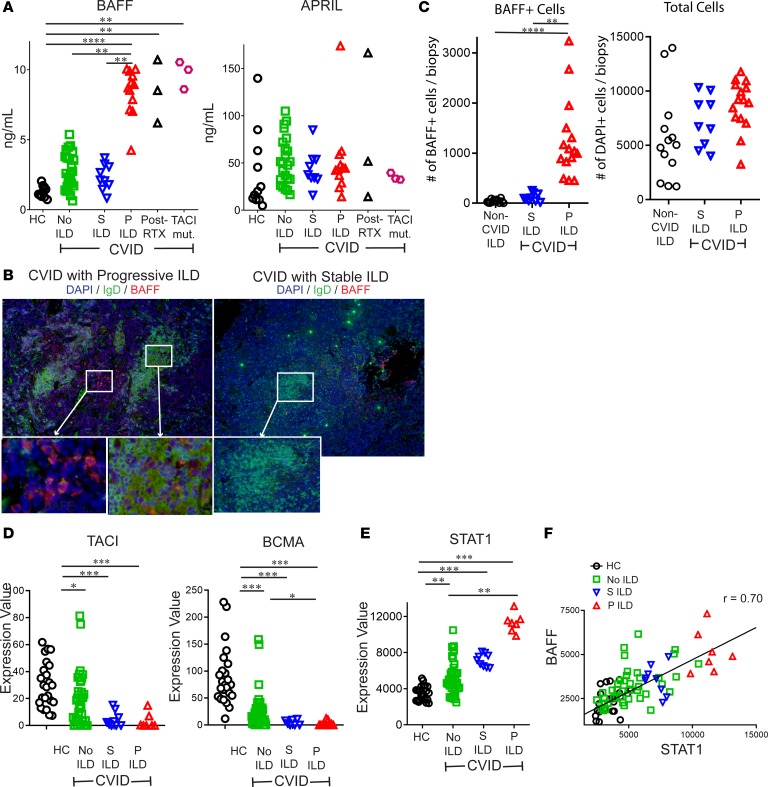
Figure 4. BAFF is elevated in CVID patients with progressive ILD and correlates with STAT1 expression.
(A) Serum BAFF, but not APRIL, was significantly increased in CVID patients with progressive (P) ILD compared with CVID with stable (S) ILD, no ILD, and healthy controls. Serum BAFF was also elevated in those treated with rituximab (RTX) and CVID ILD patients with TACI mutations (TACI mut.). (B) Immunofluorescence staining of lungs detected BAFF more prominently in patients with P ILD compared with those with S ILD. Figure representative of results from 2 non-serial sections from 6 patients. Original magnification: P ILD, ×200 and ×400 (insets); S ILD, ×100 and ×200 (insets). (C) Lung biopsies from 6 CVID patients with P ILD, 4 with S ILD, and 5 patients non–CVID ILD pulmonary lymphoid hyperplasia (2–3 non-serial sections from each patient) demonstrated significantly greater BAFF+ cells, but not total cells (DAPI+) in CVID P ILD. (D) RNA expression of TNFRSF13B (TACI) and TNFRSF17 (BCMA) is reduced in CVID patients compared with controls but does not distinguish those with P or S ILD. (E) STAT1 expression was highest in CVID P ILD patients and (F) correlated (Spearman) with expression of TNFSF13B (BAFF). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by Kruskal-Wallis test for 3-group comparison and Mann-Whitney test for 2-group comparison.