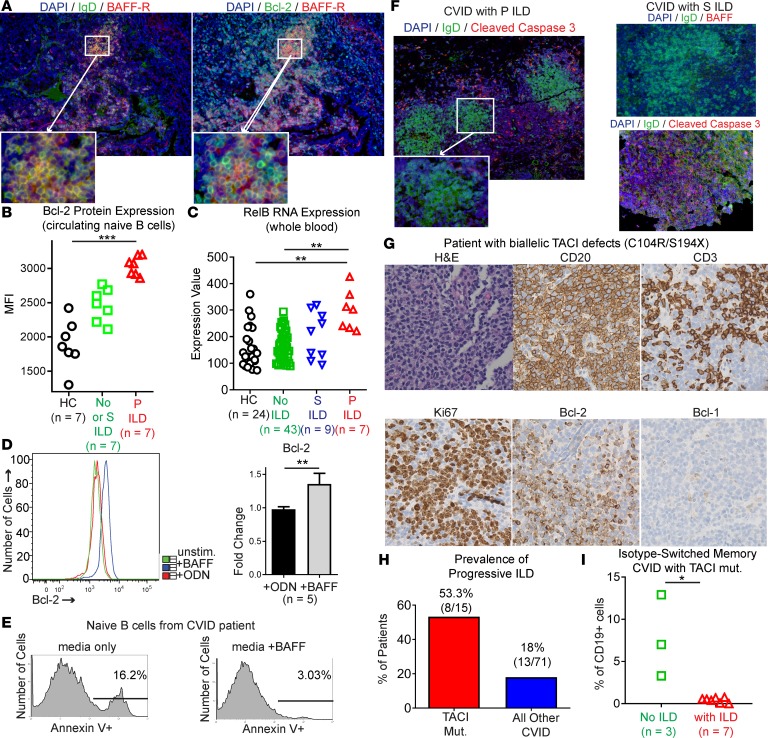
Figure 7. Naive B cells express Bcl-2 in response to BAFF-R signaling to resist apoptosis and promote progression of CVID ILD.
(A) Serial sections demonstrate that Bcl-2 colocalizes with BAFF-R within ectopic IgD+ B cell follicles in CVID ILD. Original magnification, ×200 and ×400 (insets). (B) Bcl-2 expression on circulating naive B cells is elevated in CVID with progressive (P) ILD compared with CVID with stable (S) ILD, no ILD, and healthy controls (HCs). (C) RNA expression of the noncanonical NF-κB pathway mediator RelB is elevated in whole blood of CVID patients with P ILD. (D) BAFF induces Bcl-2 expression in naive B cells from CVID patients at levels significantly greater than those induced by the TLR9 agonist ODN. (E) Addition of BAFF reduces apoptosis in culture of naive B cells from CVID patients. Data representative of 4 similar experiments. (F) The pattern of cleaved caspase-3 expression indicates that apoptosis is largely excluded from ectopic B cell follicles in CVID patients with P ILD. In contrast, lung biopsies from CVID patients with S ILD showed extensive apoptosis within ectopic B cell follicles. Data are consistent with results from 6 CVID patients. Original magnification, ×100 and ×200 (insets). (G) Biallelic defects of TACI did not prevent lymphoid hyperplasia with prominent Bcl-2–expressing B cell follicles. Original magnification, ×200. (H) Incidence of P ILD was higher in CVID patients with genetic deficiency of TACI compared with other CVID patients in our study cohort. (I) CVID patients with TACI mutations and ILD had significantly lower levels of isotype-switched memory B cells compared with CVID patients with TACI mutations but no ILD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by Kruskal-Wallis test for 3-group comparison and Mann-Whitney test for 2-group comparison.