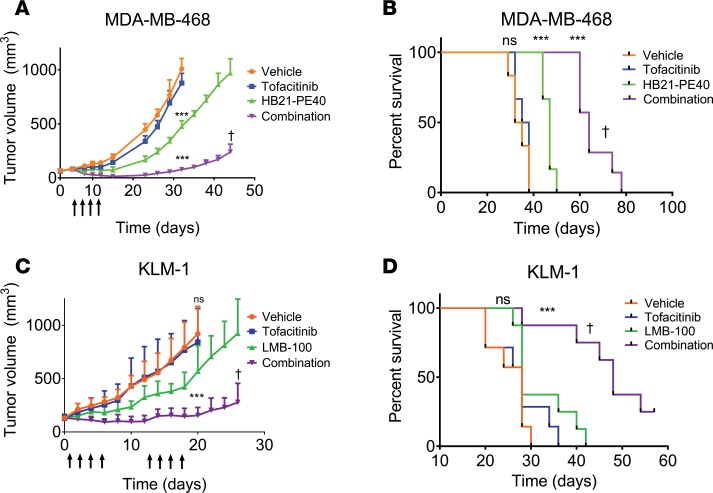
Figure 1. Tofacitinib enhances immunotoxin-mediated antitumor activity.
(A) Mice bearing MDA-MB-468 TNBC xenografts were treated with vehicle, tofacitinib alone, immunotoxin (HB21-PE40) alone, or a combination of both treatments (n = 6–7 mice per treatment group). Mice received a single treatment cycle (once every other day; arrows). Significance was calculated by 2-tailed t test at experimental endpoints. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments, showing similar results. (B) Kaplan-Meyer plot displaying time to endpoint for each treatment group of mice implanted with MDA-MB-468 tumors. Log-rank test was performed to calculate significance. (C) Mice bearing KLM-1 PDAC xenografts were treated with vehicle, tofacitinib alone, immunotoxin (LMB-100) alone, or a combination of both (n = 7–8 mice per treatment group). Mice received 2 cycles of treatment with a week in between cycles (each cycle: once per day, 4 times; arrows). Significance was calculated as above. (D) Kaplan-Meyer plot displaying time to endpoint of each treatment group for mice implanted with KLM-1 tumors. Log-rank test was performed to calculate significance. ***P < 0.001 compared with vehicle-treated; †P < 0.01 compared with immunotoxin treated (A–D). ns, not significant.