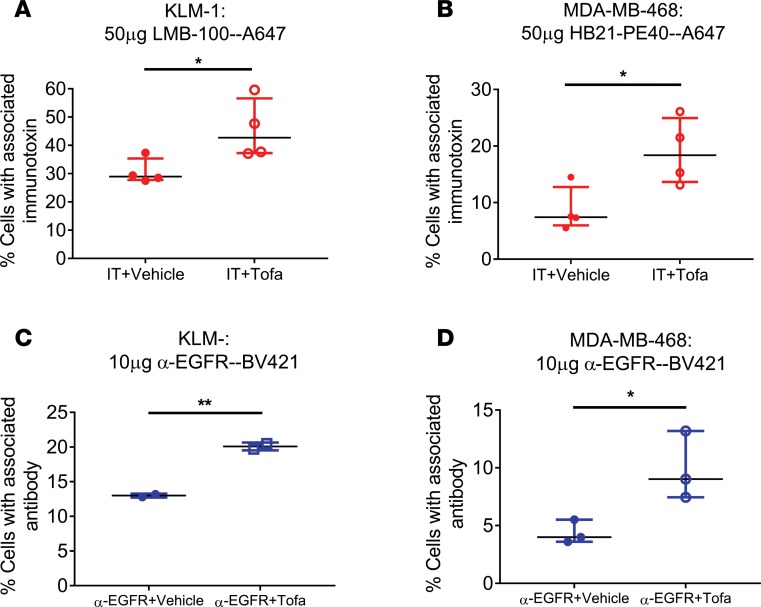
Figure 2. Tofacitinib enhances delivery of antibody-based therapeutics to cancer cells.
(A) Mice bearing KLM-1 xenografts were injected with LMB-100–A647 for 3 hours with or without tofacitinib pretreatment. Human tumor cells were identified by incubation with anti-huEGFR–BV421. The average percentage of EGFR+ immunotoxin-labeled cells for each treatment is displayed. n = 4 independent biological replicates. (B) Mice bearing MDA-MB-468 xenografts were injected with HB21-PE40–Alexa647 for 3 hours with or without tofacitinib pretreatment. The percentage of EGFR+ immunotoxin-positive cells for each treatment is displayed. n = 4 independent biological replicates. (C) Mice with KLM-1 xenografts were injected with anti-EGFR–BV421 for 3 hours with or without tofacitinib pretreatment. Human tumor cells were identified by incubation with anti–human transferrin receptor–APC. The percentage of TfnR+ cells displaying EGFR antibody signal is displayed for each treatment. n = 2 independent biological replicates. (D) Mice with MDA-MB-468 xenografts were injected with anti-EGFR–BV421 for 3 hours with or without tofacitinib. The percentage of TfnR+ cells showing EGFR antibody signal is displayed for each treatment. n = 3 independent biological replicates. (A–D) Significance of differences between antibody-based therapeutic alone and antibody-based therapeutic plus tofacitinib treatments was calculated by unpaired 2-tailed t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.