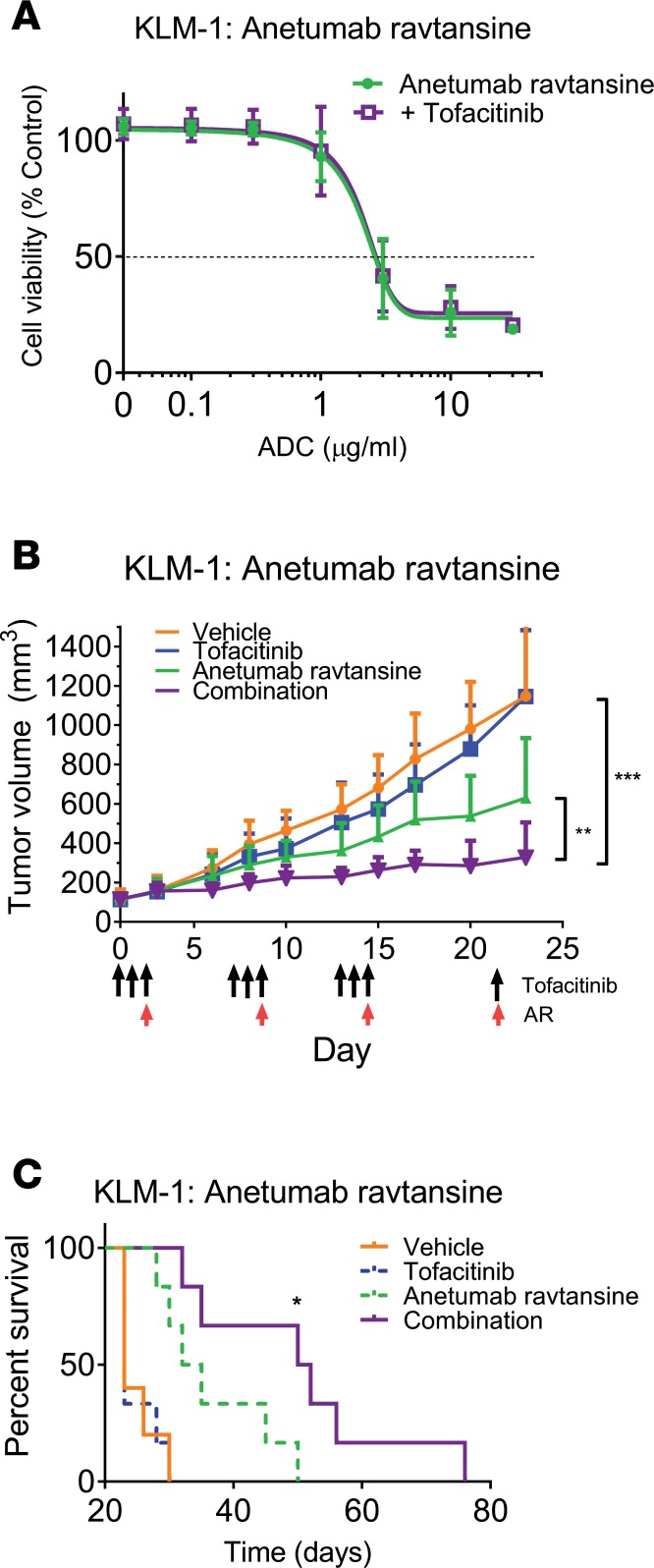
Figure 3. Tofacitinib treatment enhances the antitumor effects of an ADC in vivo.
(A) KLM-1 cells were incubated with the indicated concentration of ADC (anetumab ravtansine) and tofacitinib for 72 hours. Cell viability was measured and normalized to non–ADC-treated controls. n = 2 independent replicates performed in triplicate. (B) Mice bearing KLM-1 xenografts were treated with vehicle, tofacitinib alone, anetumab ravtansine (10 mg/kg) alone, or a combination of both (n = 5–6 mice per treatment group). Mice received 3 cycles of treatment with a week between cycles (arrows). Tumor volumes were measured and significance was calculated by unpaired 2-tailed t test between each treatment group at experimental endpoints. For KLM-1 tumors, a preliminary experiment with only 1 cycle of treatment at a lower ADC dose showed enhancement of ADC activity with tofacitinib compared with ADC alone, but of a lower magnitude (Supplemental Figure 4). (C) Kaplan-Meyer plot displaying time to death of each treatment group for mice implanted with KLM-1 tumors. Log-rank test was performed to calculate significance between anetumab ravtansine alone and anetumab ravtansine plus tofacitinib treatments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.