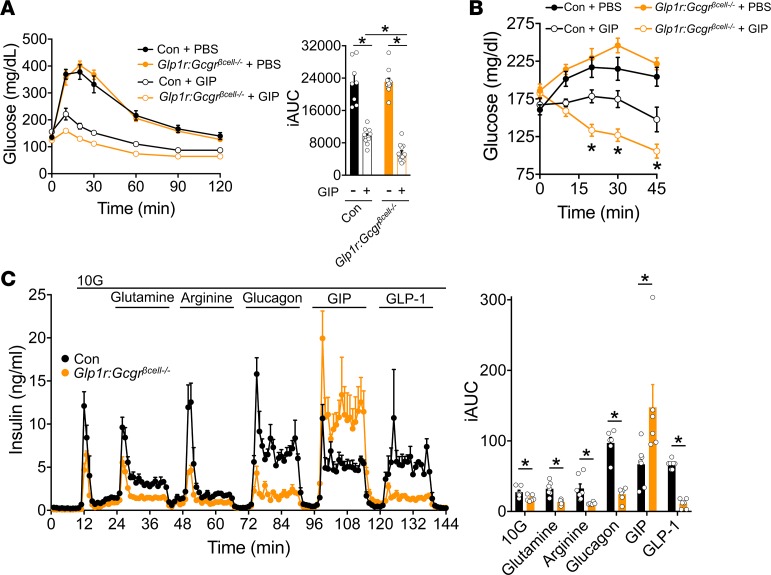
Figure 7. Gcgr:Glp1rβcell–/– mice show an increased sensitivity to GIP in vivo and ex vivo.
(A) i.p. glucose tolerance and iAUC from control (n = 11) and Gcgr:Glp1rβcell–/– (n = 13) mice on a chow-diet treated with PBS or D-Ala-GIP (4 nmol/kg) 10 minutes before glucose (1.5 mg/kg). (B) Glycemia in ambient fed control (n = 9) and Gcgr:Glp1rβcell–/– (n = 14) mice on chow diet after i.p. injection of PBS or D-Ala-GIP (4 nmol/kg). (C) Insulin secretion in response 10 mM glucose, 10 mM glutamine, 1 mM arginine, 10 nM glucagon, 3 nM GIP, and 0.3 nM GLP-1 from control (n = 7) or Gcgr:Glp1rβcell–/– islets (n = 6). *P < 0.05. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed by a 2-way ANOVA of glycemic curves (A and B) and the iAUCs (A and C).