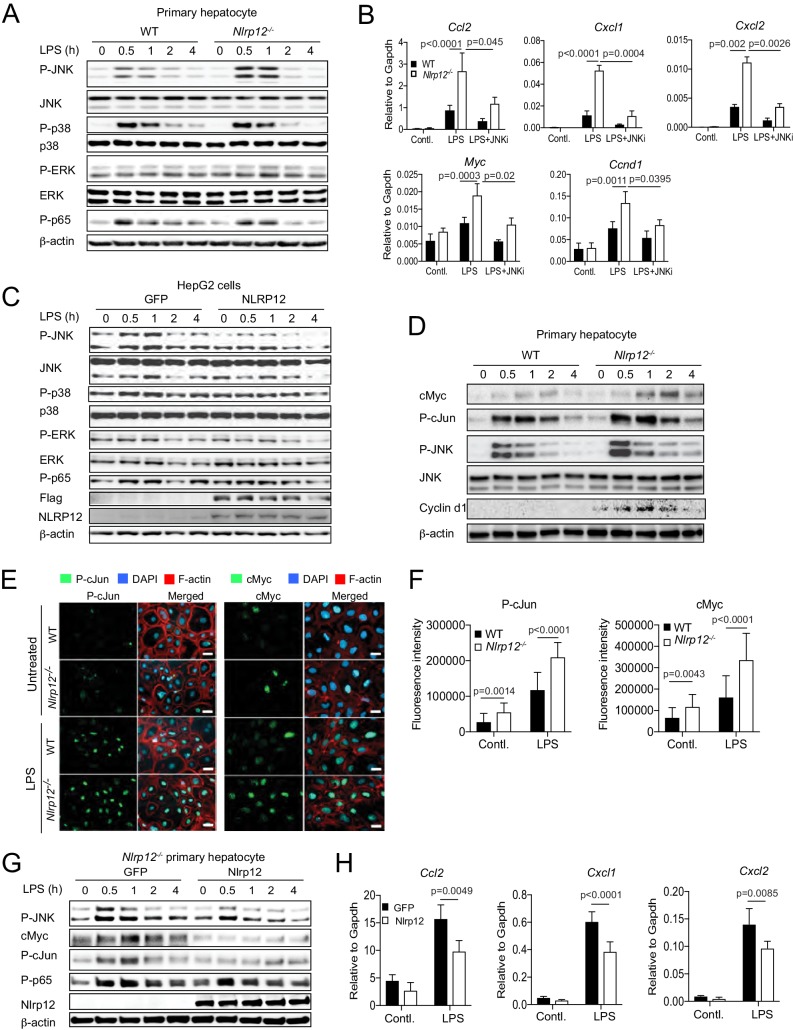
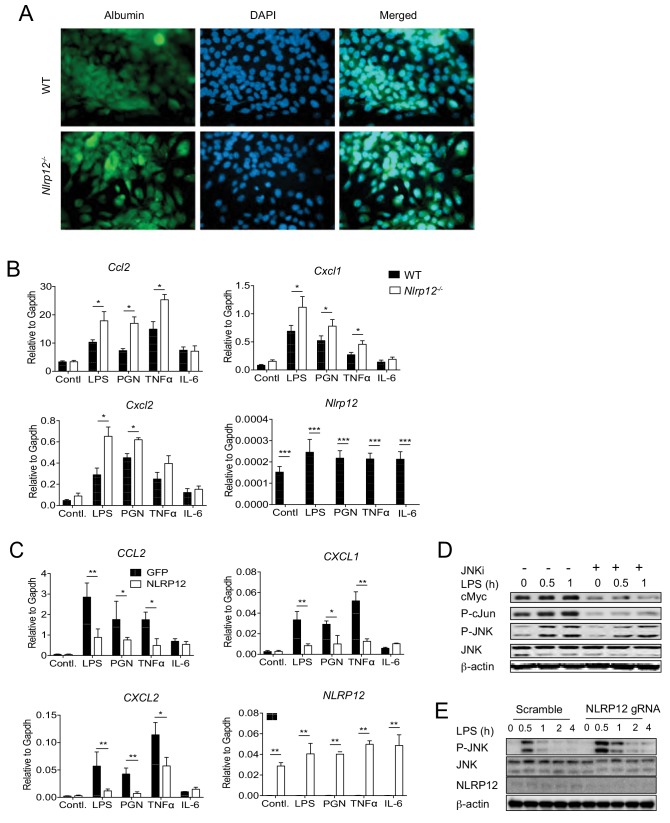
Figure 6. NLRP12 downregulates JNK activation in hepatocytes.
(A) Primary hepatocytes from healthy WT and Nlrp12-/- mouse livers were isolated and cultured. Hepatocytes were stimulated with LPS for the indicated time and analyzed for the activation of JNK, p38, ERK, and p65 by Western blotting. (B) Primary hepatocytes from healthy WT and Nlrp12-/- mouse livers were stimulated with LPS in the presence of absence of JNK inhibitor. The expression of inflammatory and proliferative molecules was measured by real-time qPCR. Data represent means ± SD (n = 3 replicates). Statistical difference was determined by two-tailed unpaired t-test. (C) HepG2 cells stably expressing either GFP or NLRP12 were stimulated with LPS and analyzed for the activation of JNK, p38, ERK, and p65 by Western blotting. (D) Primary hepatocytes isolated from untreated WT and Nlrp12-/- mouse livers were stimulated with LPS for the indicated time periods and analyzed for cMyc, P-cJun, Cyclin d1, and P-JNK by Western blotting. (E–F) Primary hepatocytes grown on coverslip were treated with or without LPS for 1 hr and immunostained for P-cJun (green) and cMyc (green). Cellular morphology was visible with filamentous actin (F-actin) staining (red). DAPI (blue) was used for nuclear staining. (F) P-cJun and cMyc fluorescence intensities were measured by Image J software. Data represent means ± SD (n = 20) and is representative of three independent experiments. Statistical difference was determined by two-tailed unpaired t-test. (G–H) Nlrp12-/- primary hepatocytes were transiently transfected with either GFP or Nlrp12 constructs followed by stimulation with LPS. The levels of P-JNK, cMyc, P-cJun, and P-p65 were measured by Western blotting (G) and the expression KC (Cxcl1), MIP2 (Cxcl2), and MCP1 (Ccl2) was analyzed by real-time qPCR (H). Data represent means ± SD (n = 3 replicates) and is representative of three independent experiment. Statistical difference was determined by two-tailed unpaired t-test.