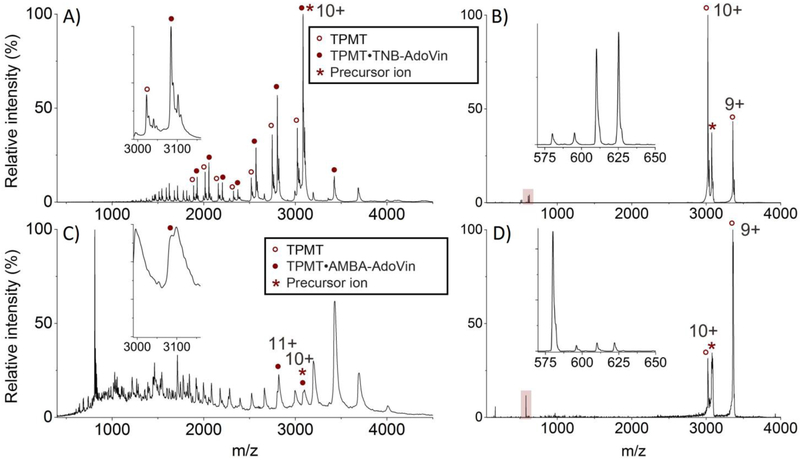
Figure 2.
(A) In vitro [TPMT•TNB-AdoVin] complex and apo-TPMT were detected in multiple charge states using native mass spectrometry. In this simple system, the bound and apo- forms of TPMT were easily distinguished (inset). (B) Collision induced dissociation (CID) at a collision energy of 500 eV of the 10+ charged precursor ion of the [TPMT•TNB-AdoVin] complex (*) in (A). This collision resulted in some apo-TPMT with the 10+ and 9+ charge states and the TNB-AdoVin adduct (highlighted and inset). Doublets observed in the TNB-AdoVin spectra are due to a mixture of natural and isotopically labeled AdoVin (+15 Da). (C) [TPMT•AMBA-AdoVin] complex was identified in multiple charge states from whole cells without purification. In this complex matrix, bound and apo- forms of TPMT were not resolved (inset). (D) CID at a collision energy of 500 eV of the 10+ charged precursor ion of the [TPMT•AMBA-AdoVin] complex (*) in (C). After collision, again, multiple charge states for the apo-enzyme were observed along with the AMBA-AdoVin adduct (highlighted and inset). In this case, isotopically labeled probe was not used, resulting in a single peak. Isotopically-labeled spectra were previously reported. [22]