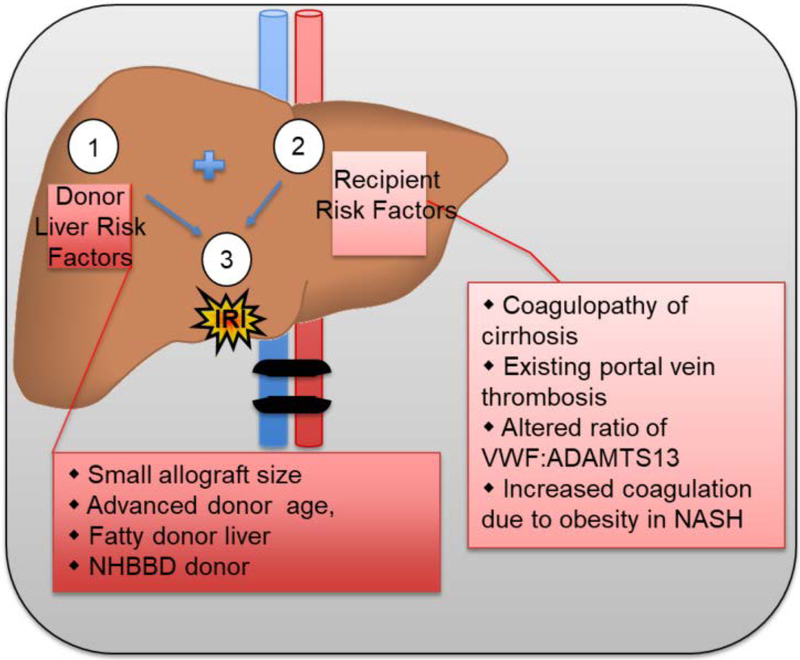
Figure 2: Surgical, Donor, and Recipient factors that contribute to risk of IRI.
(1) Risks of IRI inherent to liver transplantation include: organwide ischemia during clamping and resection of donor organ, cold storage, re-anastomosis and circulation of widespread inflammatory factors, increased ischemic time. (2) Donor Liver risk factors can increase the severity of IRI: small allograft, advanced age, especially age >70, donor fatty liver, especially macrosteatosis > 30%, cause of donor death, NHBBD donor, use of marginal organs due to donor scarcity. (3) Recipient risk factors can further increase the severity of IRI: cirrhosis or hepatic fibrosis induced coagulopathy, nutritional coagulopathy, portal vein or hepatic artery thrombosis, altered VWF:ADAMTS13 ratio, history of NASH.