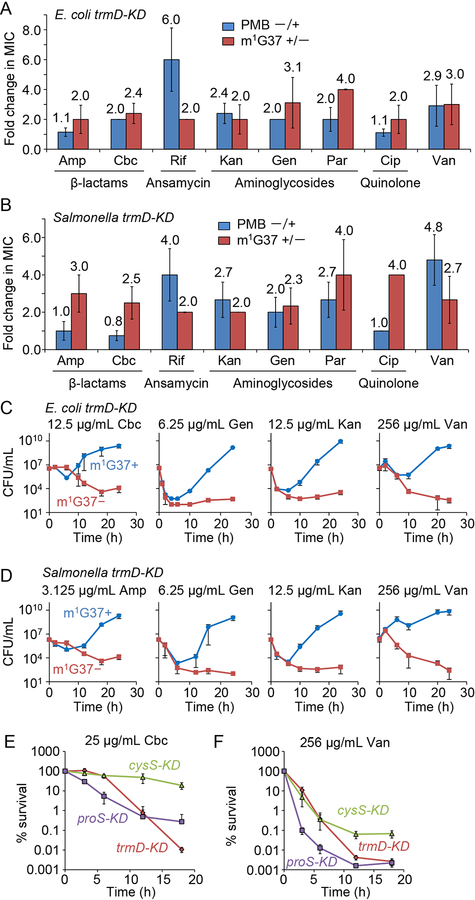
Figure 4: m1G37 deficiency sensitizes trmD-KD cells to multiple antibiotic classes.
A,B) m1G37− cells had at least 2-fold lower MICs than m1G37+ cells. The fold-decrease in MIC of each antibiotic was calculated for E. coli (A) and Salmonella (B) trmD-KD cells as the ratio of the MIC in m1G37+ and m1G37− cells (red) and was compared with the relative decrease of m1G37+ cells upon treatment with polymyxin B (PMB) at 0.25X MIC (blue). Overnight cultures were inoculated into fresh LB at 106 CFUs/mL and incubated with an antibiotic in serial dilutions. After 18 h of incubation at 37 °C, cell densities lower than OD600 = 0.15 were scored as no growth. Fold-changes are taken from Figure S6A, where data and errors are mean ± SD, n > 4. Amp, ampicillin; Cbc, carbenicillin; Rif, rifampicin; Kan, kanamycin; Gen, gentamicin; Par, paromomycin; Cip, ciprofloxacin; Van, vancomycin.
C,D) Time-kill analyses of E. coli (C) and Salmonella (D) trmD-KD cells indicate that m1G37+ cells (blue) recovered from antibiotic exposure, but that m1G37− (red) cells did not. Overnight cultures (106 CFUs/mL) were inoculated into fresh LB with an antibiotic at the indicated concentration and grown at 37 °C. Dat a and error bars show mean ± SD, n > 3.
E,F) Percent survival of m1G37− E. coli trmD-KD cells upon exposure to 25 μg/mL carbenicillin (E) or 256 μg/mL vancomycin (F), showing a decrease in survival comparable to proS-KD cells but faster and to a greater extent compared with cysS-KD cells. Data and error bars show mean ± SD, n > 3.
See also Figure S6.