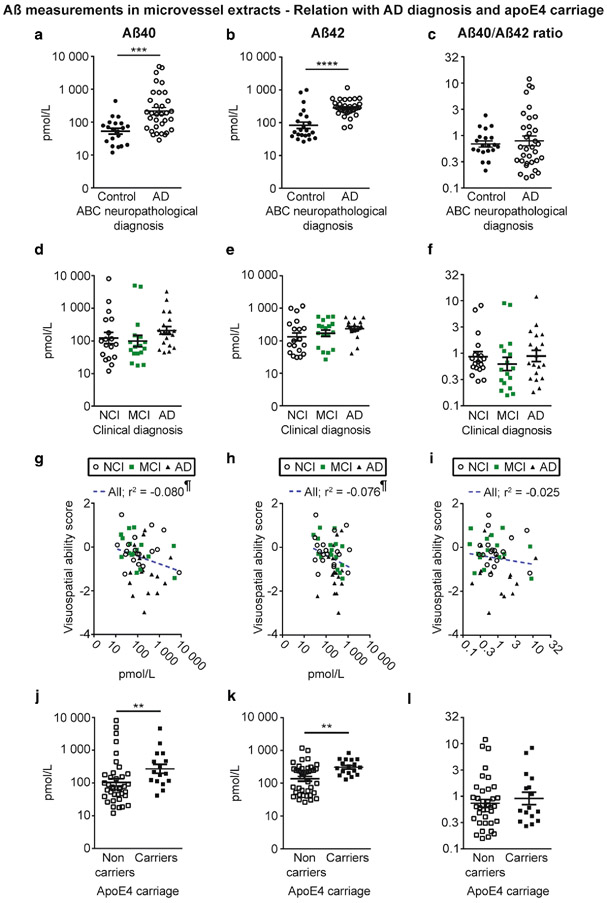
Fig. 3.
Aβ40 and Aβ42 concentrations in brain microvessels are increased in persons with AD and in apoE4 carriers. Concentrations of Aβ40, Aβ42 and Aβ40/Aβ42 ratios were determined in brain microvascular extracts by ELISA. a-c) Participants were divided according to their neuropathological diagnosis based on the ABC criteria; d-f) their clinical diagnosis and j-l) their apoE4 allele carriage. We observed increased concentrations of Aβ in individuals with a neuropathological diagnosis of AD (a, b) and in apoE4 carriers (j, k). For all groups, no significant variation was found for the Aβ40/Aβ42 ratios (c, f and l). Data were log transformed for statistical analysis and are represented as scatterplots with a logarithmic scale. Horizontal bars indicate mean ± S.E.M. Statistical analysis: Mann-Whitney test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001. Correlative analysis revealed that Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels in microvessel extracts were both negatively associated with visuospatial ability scores (g, h). Statistical analysis: Pearson correlation coefficient. ¶ p < 0.05. Abbreviations: AD, Alzheimer’s disease; MCI, mild cognitive impairment; NCI, healthy controls with no cognitive impairment