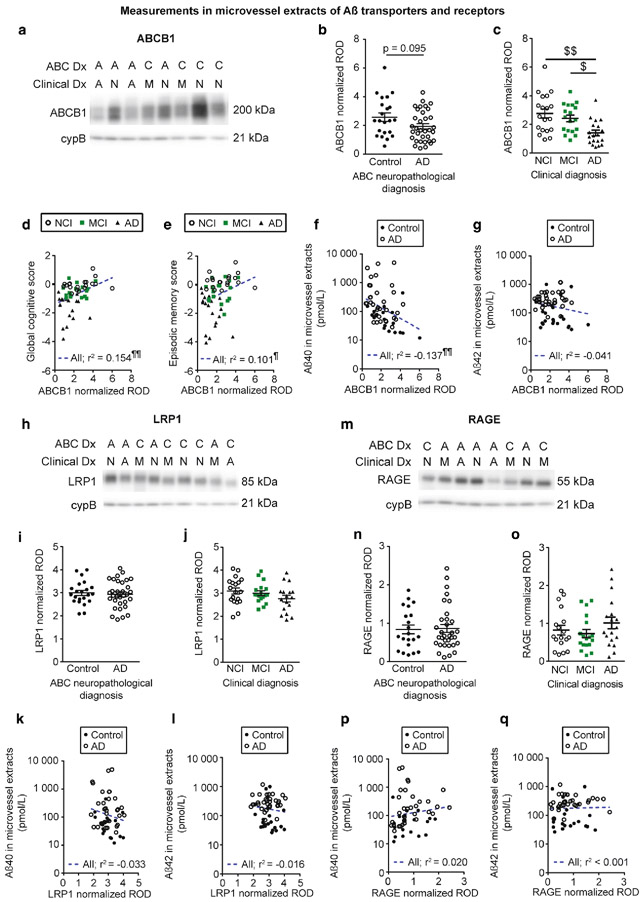
Fig. 5.
Aβ efflux transporter ABCB1 is reduced in vascular fractions from individuals with AD. ABCB1 (p-glycoprotein), LRP1 and RAGE levels in microvessel extracts were determined by Western blot. Data were normalized with cyclophilin B. Representative immunoblotting examples for ABCB1, LRP1 and RAGE (panels a, h and m). All samples, loaded in a random order, were run on the same immunoblot experiment for quantification. Consecutive bands are shown. No difference was found when participants were divided according to their AD neuropathological diagnosis (panels b, i and n). When individuals were grouped based on their clinical diagnosis, a significant reduction was noted for ABCB1 in AD while no difference was observed for LRP1 and RAGE (panels c, j and o). Statistical analysis: Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance followed by a Dunn’s post hoc test. $ p < 0.05, $$ p < 0.01. ABCB1 levels in microvessel extracts were positively associated to global cognition and episodic memory (panels d and e). In microvessel extracts, among transporters investigated only ABCB1 levels were inversely correlated to Aβ40 content (Panel f). No significant correlation was observed between Aβ42 concentrations in microvessel extracts and any of the transporter investigated (panels g, l and q). Statistical analysis: Pearson correlation coefficient. ¶ p < 0.05, ¶¶ p < 0.01. Abbreviations: A/AD, Alzheimer’s disease; ABC Dx, ABC neuropathological diagnosis; C, control; Clinical Dx, clinical diagnosis; cypB, cyclophilin B; M/MCI, mild cognitive impairment; N/NCI, healthy controls with no cognitive impairment; ROD, relative optical density