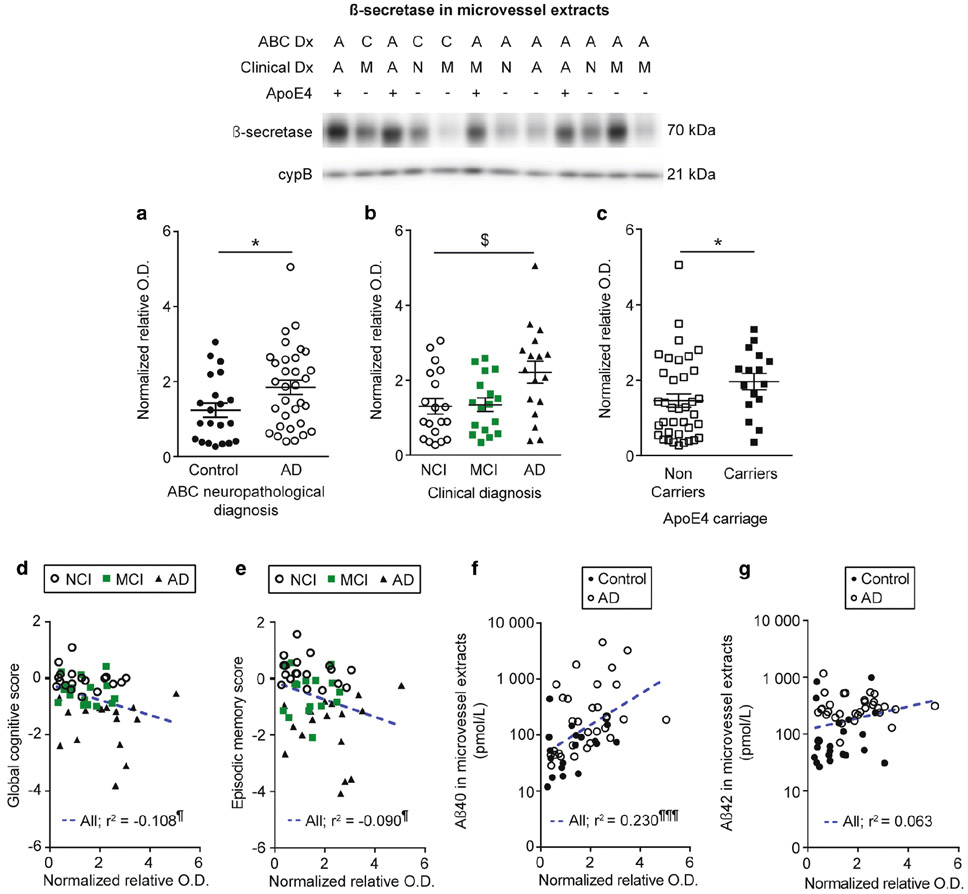
Fig. 8.
β-secretase levels are increased in individuals with AD and in apoE4 carriers, and are correlated to cognition and Aβ40 peptides in microvessel extracts. β-secretase (BACE1) levels in microvessel extracts were determined by Western blot. Data were normalized with cyclophilin B. a-c) Participants were divided according to a) their AD neuropathological diagnosis; b) their clinical diagnosis and c) their apoE4 allele carriage. We observed an increase in BACE1 levels in individuals with a neuropathological diagnosis of AD (panel a) or a clinical diagnosis of AD (panel b). We also observed an increase for apoE4 carriers compared to non-carriers (panel c). All samples, loaded in a random order, were run on the same immunoblot experiment. Consecutive bands were taken for the representative photo example. Data are represented as scatterplots. Horizontal bars indicate mean ± S.E.M. Statistical analysis: Mann Whitney test, * p < 0.05; Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance followed by a Dunn’s post hoc test, $ p < 0.05. Linear regression analyses showed that BACE1 levels were negatively associated with global cognition (panel d) and episodic memory (panel e). In addition, BACE1 levels were positively correlated to Aβ40 concentrations in microvessel extracts (panel f). In addition, a trend towards a positive correlation was observed for Aβ42 (panel g). Statistical analysis: Pearson correlation coefficient. ¶ p < 0.05, ¶¶¶ p < 0.001. Abbreviations: −, ApoE4 non-carrier; +, ApoE4 carrier; A/AD, Alzheimer’s disease; ABC Dx, ABC neuropathological diagnosis; C, control; Clinical Dx, clinical diagnosis; cypB, cyclophilin B; M/MCI, mild cognitive impairment; N/NCI, healthy controls with no cognitive impairment; relative O.D., relative optical density.