Figure 9.
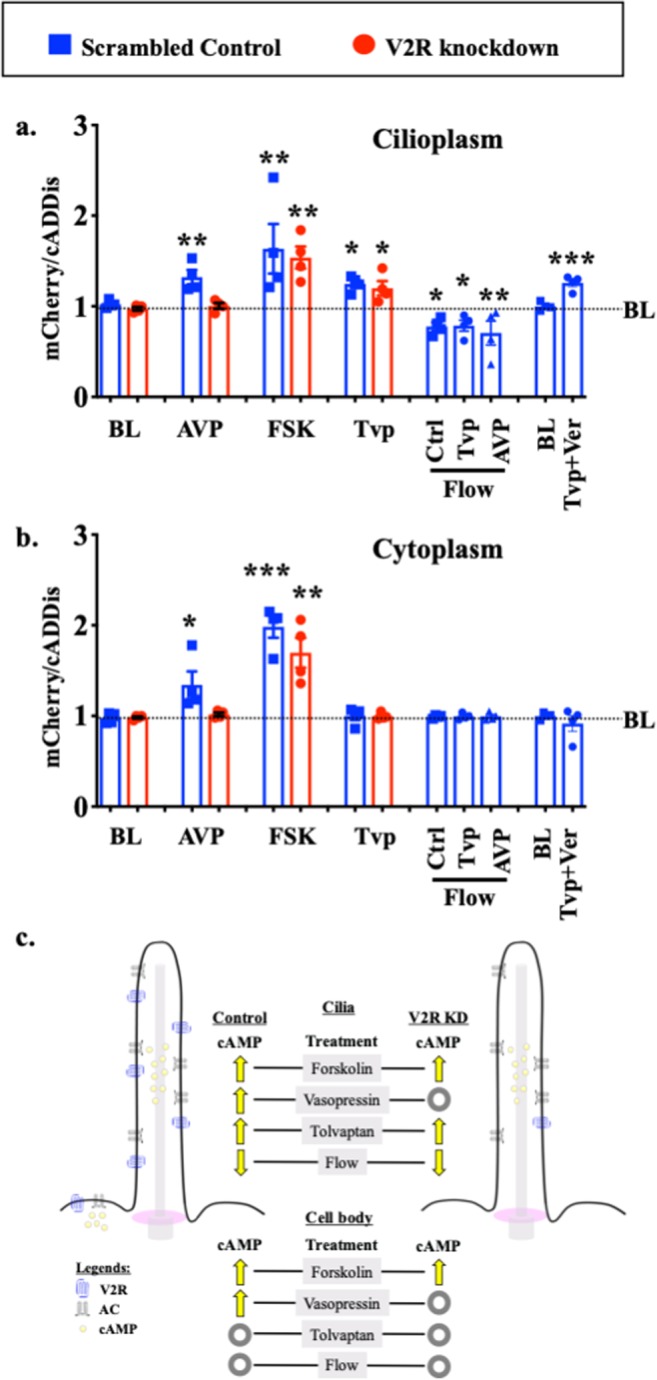
Cilioplasmic and cytoplasmic cAMP levels are differentially regulated. Peak cAMP increase in response to each stimulus is summarized in the bar graph for (a) cilioplasm and (b) cytoplasm. N = 4 experiments for each group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, and ***P < 0.0001 compared to the baseline (BL) level prior to stimulus; AVP = arginine vasopressin; FSK = forskolin; Tvp = tolvaptan; Ctrl = control; Ver = verapamil. (c) Vasopressin receptor type-2 (V2R) is localized to primary cilia in renal epithelia, and V2R activation with vasopressin increases adenylyl cyclase (AC) activity. Tolvaptan but not vasopressin elicits a cAMP increase in V2R-knockdown in primary cilium. Unlike tolvaptan which shows cilia-specific cAMP response, AC activator (forskolin) and vasopressin elicit cAMP responses in both cilioplasm and cytoplasm. Cilioplasmic but not cytoplasmic cAMP signaling is repressed below basal levels when cilia bend by fluid-flow. These responses indicate that a cilium may function as a distinct cAMP microdomain, independent from cytoplasmic cAMP.
