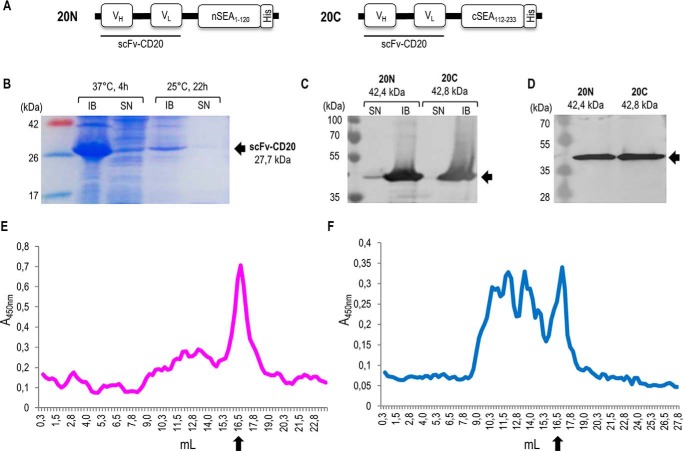
Figure 5.
Design and production of split SEA2/scFv-CD20 fusion proteins. A, schematic representation of fusion proteins scFv–CD20/nSEA2 (20N) and scFv–CD20/cSEA2 (20C) in pET-19b vector. VH, variable region of heavy chain; VL, variable region of light chain; (G4S)2, glycine-serine linker; split SEA variant 2 fragments nSEA1–120 and cSEA112–233; His, histidine tag. B, SDS-PAGE analysis of scFv–CD20 produced in E. coli after induction with 1 mm IPTG. Representative soluble (SN) and insoluble (IB) fractions after production at different temperatures and times are shown. C, Western blot analysis of fusion proteins scFv-CD20/nSEA2 and scFv-CD20/cSEA2 produced in E. coli after induction with 0.2 mm IPTG. Soluble (SN) and insoluble (IB) fractions after 4 h production at 37 °C are shown. D, Western blot analysis of purified and refolded fusion proteins scFv–CD20/nSEA2 and scFv–CD20/cSEA2. E and F, analysis of fusion proteins scFv–CD20/nSEA2 (E) and scFv–CD20/cSEA2 (F) by size-exclusion chromatography. Arrows indicate the monomeric form of fusion proteins at the expected molecular mass of 42 kDa.