Figure 4.
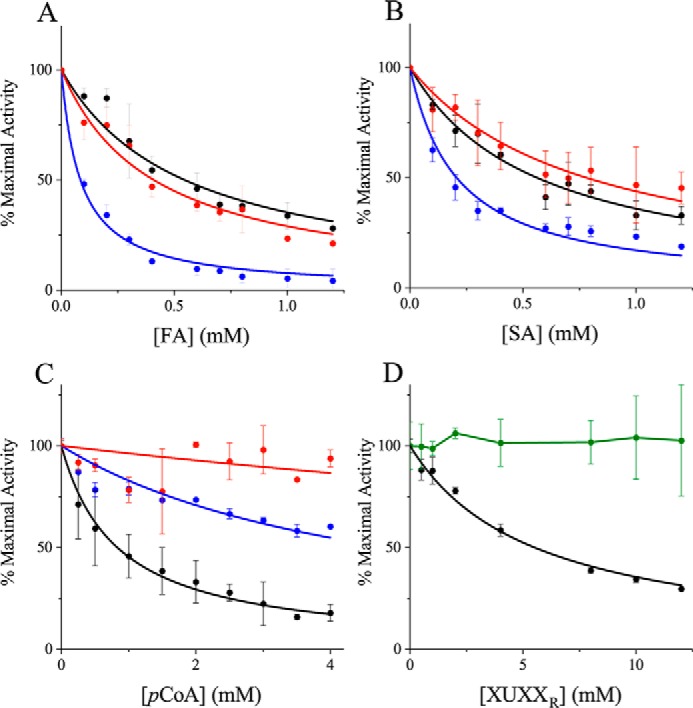
Inhibition of TtCE15A with aromatic compounds and xylooligosaccharides. Inhibition of the WT enzyme activity (black) compared with F174A (blue) and F174D (red) by FA (A), SA (B), and pCoA (C) and inhibition of TtCE15A WT activity (black) compared with W376A (green) by XUXXR (D) are shown. The inhibitors were added in increasing concentrations to 0.4 mm BnzGlcA, up to 1.2 mm FA or SA, 4 mm pCoA, and 12 mm XUXXR. The inhibitory effect of the compounds was calculated by nonlinear regression, fitting Equation 1 (see “Experimental procedures”) to the data (not possible for W376A with XUXXR). Error bars represent S.D. from the mean value of duplicate measurements. The data are normalized to facilitate comparison, where 100% maximal activity corresponds to the following rates (v/[E]t): 11.1 (WT), 1.7 (F174A), 0.3 (F174D), and 3.0 s−1 (W376A). Similar or even stronger inhibition by FA and SA was observed for the Phe-174 variants compared with the WT enzyme. However, the variants lacking Phe-174 or Trp-376 were less inhibited by pCoA and XUXXR than the WT enzyme.
