Figure 2.
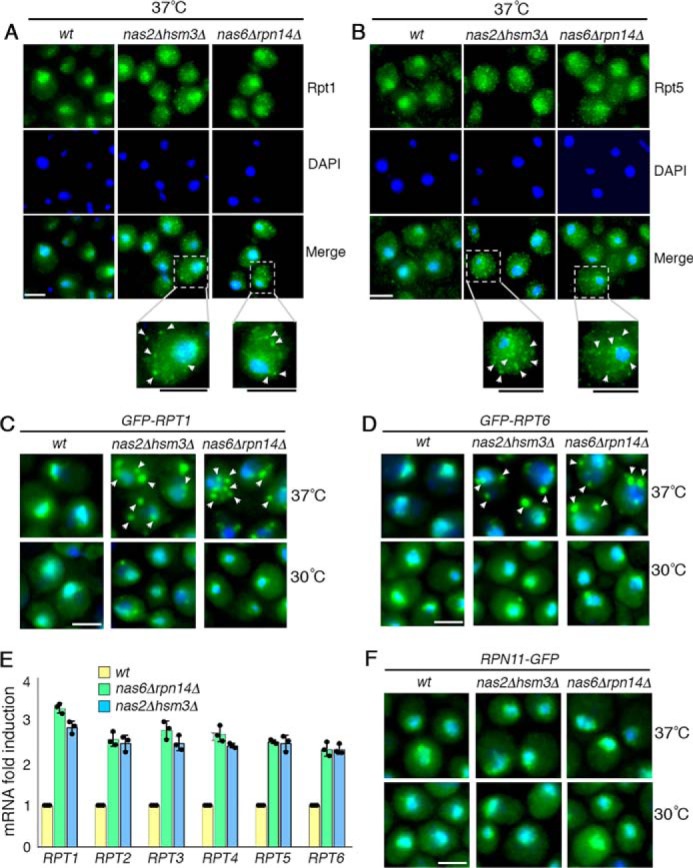
During early-stage Rpt ring assembly, excess Rpt subunits are sequestered into puncta. A–D, excess Rpt subunits are sequestered into puncta during early-stage Rpt ring assembly. Indicated yeast strains were exposed to heat stress at 37 °C for 4 h (A and B). Yeast cells were imaged using epi-fluorescence microscopy to visualize Rpt1 and Rpt5, using antibodies specific to these subunits (A and B). Scale bar, 5 μm for all panels. For insets, scale bars are shown as black lines directly below the panels. C and D, GFP-tagged Rpt1 and Rpt6 are expressed from their endogenous chromosomal loci and were visualized at 30 °C (bottom panels) and then after 15 min of heat stress at 37 °C (top panels). DAPI staining indicates nuclei. Arrowheads indicate cytoplasmic punctate structures of Rpt subunits. Scale bar, 5 μm for all panels. E, increased mRNA levels of all six Rpt subunits in the chaperone deletion mutants. Quantitative real-time PCR results for RPT subunits were normalized to ACT1. Fold induction of RPT subunit mRNA in the indicated chaperone deletion mutants was calculated relative to WT (average ± S.D.; n = 3, biological replicates); individual data points are indicated as dots. F, lid subunit, Rpn11, does not form puncta and exhibits normal nuclear localization. Experiments were conducted as in C and D. Scale bar, 5 μm for all panels.
