Figure 2.
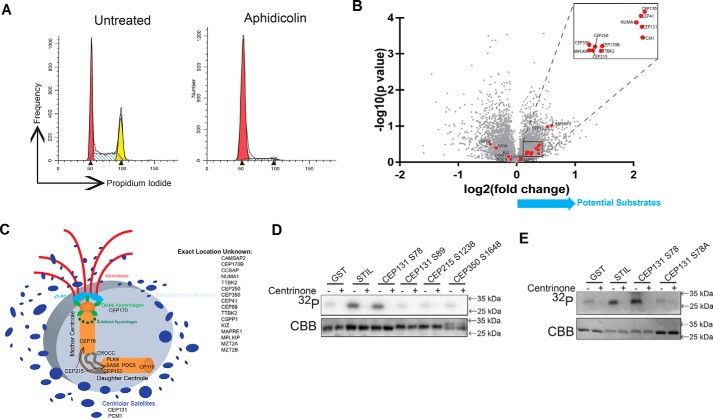
PLK4 phosphorylates CEP131 Ser-78. A, cell cycle profile of cells arrested with aphidicolin to enrich RPE PLK4 AS cells in the G1/S transition, which is when centriole duplication occurs and therefore when PLK4 is active. These cells were utilized for MS. B, volcano plot of −log10(p value) versus log2(-fold change) for the centrosome components (red dots) that were identified in the MS screen. C, diagram of the centrosome showing where each of these proteins is thought to localize; derived from Ref. 82. D, GST-tagged peptides and PLK4 kinase domain were purified from Escherichia coli and utilized for in vitro kinase assays. GST serves as a negative control, and STIL serves as a positive control. Centrinone B is a PLK4 inhibitor. E, an S78A mutation was created in the CEP131 peptide and purified for in vitro kinase assay to confirm that PLK4 phosphorylates CEP131 Ser-78.