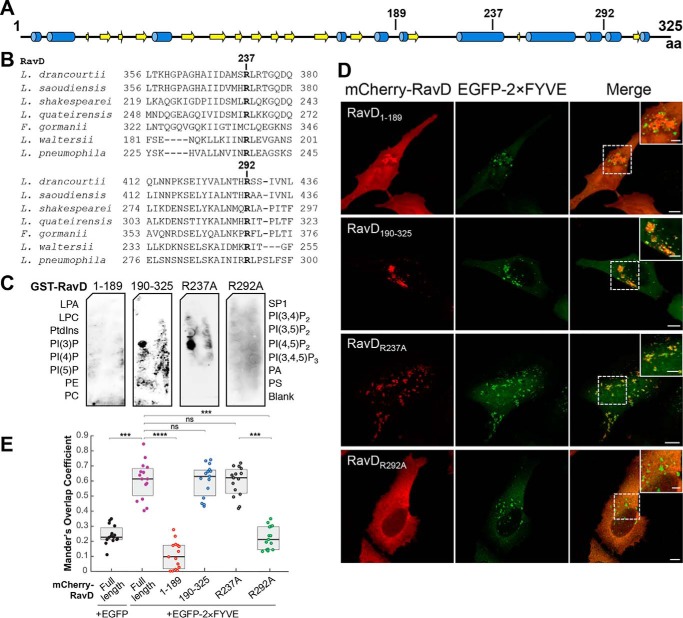
Figure 2.
The PI(3)P binding region of RavD is positioned within a C-terminal region. A, schematic of the predicted secondary structure of RavD (obtained using the JPred Protein Secondary Structure Prediction Server) (blue, α helix; yellow, β sheet); the position of relevant amino acid (aa) residues is marked. B, alignment of RavD's conserved arginine residues in the indicated Legionella species. C, protein–lipid overlay assays show that the GST-RavD190–325 and GST-RavDR237A variants recognize PI(3)P whereas GST-RavD1–189 and GST-RavDR292A do not. LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphocholine; PtdIns, phosphatidylinositol; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; SIP, sphingosine-1-phosphate; PI, phosphatidylinositol; P, phosphate; P2, biphosphate; P3, triphosphate; PA, phosphatidic acid; PS, phosphatidylserine. D, confocal images of HeLa cells transiently co-transfected with plasmids encoding either EGFP-2×FYVE and variants mCherry-RavD190–325, mCherry-RavD1–189, GST-RavDR237A, or RavDR292A. Scale bars = 10 μm (insets, 2 μm). Confocal images and assays are representative of at least two independent experiments with similar outcomes. E, Mander's overlap coefficient for fluorescence signals of EGFP-tagged and mCherry-tagged proteins, as specified. The plot shows the median (black vertical line) and interquartile range (25–75) (gray box) from 15 different cells for each condition. Individual dots represent the Mander's overlap coefficient obtained from a single cell. ***, p ≤ 0.001; ****, p ≤ 0.0001; ns, not significant.