Figure 3.
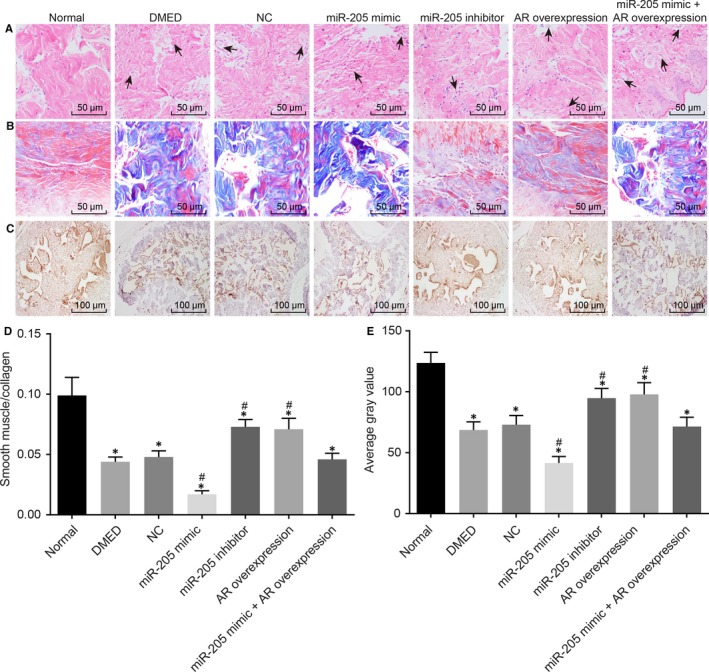
Down‐regulation of miR‐205 or overexpression of AR could prevent the pathological progression of DMED and inhibit the fibrosis of corpus cavernosum. A, pathological changes of cavernous bodies of rats treated with miR‐205 mimic, miR‐205 inhibitor, AR overexpression, and miR‐205 mimic +AR overexpression were observed by hematoxylin and eosin staining with the arrow indicating the diseased tissue (200 ×), the arrow indicates the diseased tissue; B, smooth muscle density in cavernous bodies of rats treated with miR‐205 mimic, miR‐205 inhibitor, AR overexpression, and miR‐205 mimic +AR overexpression was observed by Masson staining (400 ×); C, Immunohistochemical staining was applied to compare the positive expression rate of AR in the cavernous bodies of rats treated with miR‐205 mimic, miR‐205 inhibitor, AR overexpression, and miR‐205 mimic +AR overexpression (200 ×); D, statistical analysis of smooth muscle density measured by Masson staining; E, statistical analysis of AR positive expression in the cavernous bodies of rats treated with miR‐205 mimic, miR‐205 inhibitor, AR overexpression and miR‐205 mimic +AR overexpression; *, P < 0.05 vs the normal group; #, P < 0.05 vs the DMED group and the NC group; measurement data were expressed as mean ± SD; data in each group were analysed with ANOVA; the sample size of each group was 10; the experiment was repeated three times; DMED, erectile dysfunction rats with diabetic mellitus; miR‐205, microRNA‐205; AR, androgen receptor; NC, negative control.
