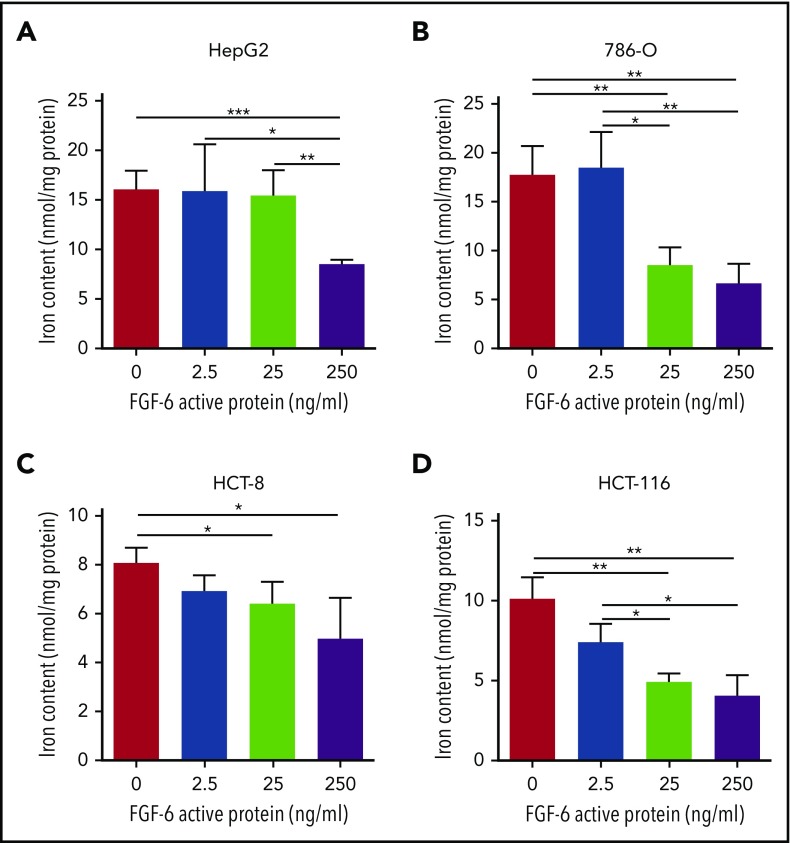
Figure 3.
FGF-6 active protein dosage effect on intracellular iron concentration. A ferrozine assay was applied for the evaluation of total cell iron content in HepG2 (human liver hepatocellular carcinoma cell line), 786-O (human kidney adenocarcinoma cell line), HCT-8 (human ileocecal colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line), HCT116 (human colon carcinoma cell line), and HFF-1 (human skin fibroblast cell line) with 10 μM FAC and 500 μM ascorbate in cell culture media, respectively, with different concentrations of FGF-6 active protein (0 ng/mL, 2.5 ng/mL, 25 ng/mL, and 250 ng/mL). Control group was treated with ascorbate alone. After 48-hour incubation, cells were lysed and iron contents were determined with the ferrozine assay. (A) Total iron content in HepG2 cells with increasing FGF-6 protein concentration. (B) Total iron content in 786-O cells with increasing FGF-6 protein concentration. (C) Total iron content in HCT-8 cells with increasing FGF-6 protein concentration. (D) Total iron content in HCT-116 cells with increasing FGF-6 protein concentration. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001.