Figure 3:
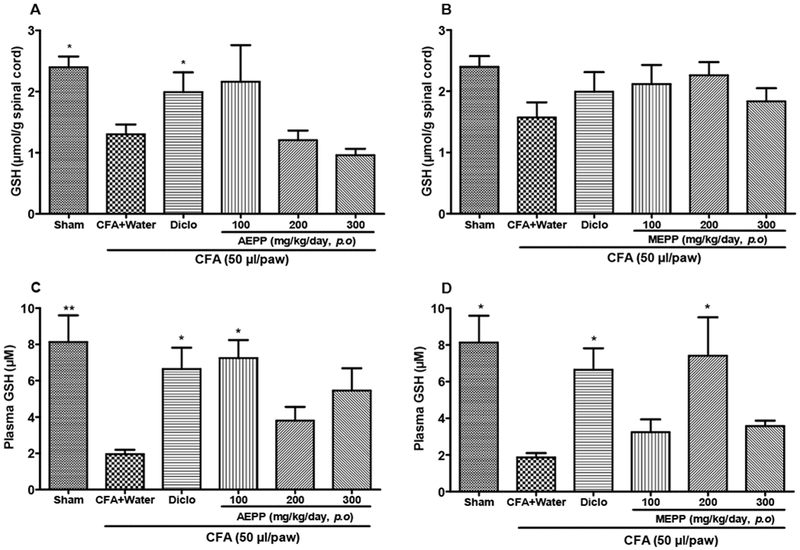
Effects of the aqueous (AEPP) and methanol (MEPP) extracts of Paullinia pinnata on the glutathione (GSH) content in the spinal cord and plasma of CFA-injected animals. NSAID diclofenac (5 mg/kg/day) is included as a positive control for anti-inflammatory effects. (A) GSH levels in the spinal cord decreased significantly after treatment with diclofenac. There was a trend for decreased GSH with AEPP 100 treatment that went away with increasing concentration. (B) MEPP treatment fails to alter GSH levels in the spinal cord. (C) AEPP 100 and diclofenac significantly reverse CFA induced GSH depletion in the plasma. (D) MEPP 200 and diclofenac MEPP significantly reverse CFA induced GSH depletion in the plasma. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of 6 individual rats, *p<0.05, **p< 0.01 significant difference compared to negative control group (CFA+Water) using 1-Way ANOVA with Tukey as post hoc test.
