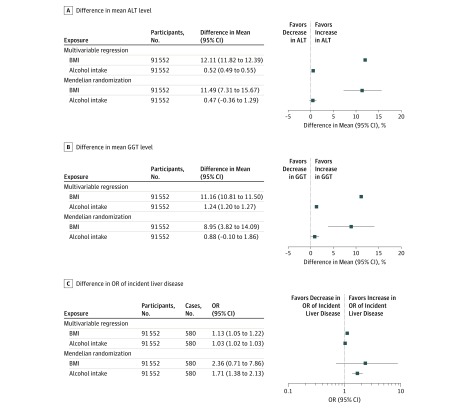
Figure 3. Multivariable and Mendelian Randomization Analyses of the Individual Associations of Body Mass Index (BMI) and Alcohol Consumption With Liver Enzyme Levels Associated With Injury and Incident Liver Disease.
A, The percentage difference in mean alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level per 1-SD higher BMI or per 1 U/wk increase in alcohol consumption. B, The percentage difference in mean γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT) level per 1-SD higher BMI or per 1-U increase in alcohol consumption. C, The difference in odds ratio (OR) of incident liver disease per 1-SD higher BMI or per 1-U/wk increase in alcohol consumption. The BMI is measured as age and sex SD units. Alcohol measured as units of alcohol consumed per week, where 1 U is equivalent to 12 g of alcohol. Multivariable analyses were adjusted for age, sex, smoking, educational level, income, and physical activity. Mendelian randomization used weighted allele score for BMI and ADH1B alleles for alcohol consumption. Prevalent cases of liver disease were excluded from all analyses.