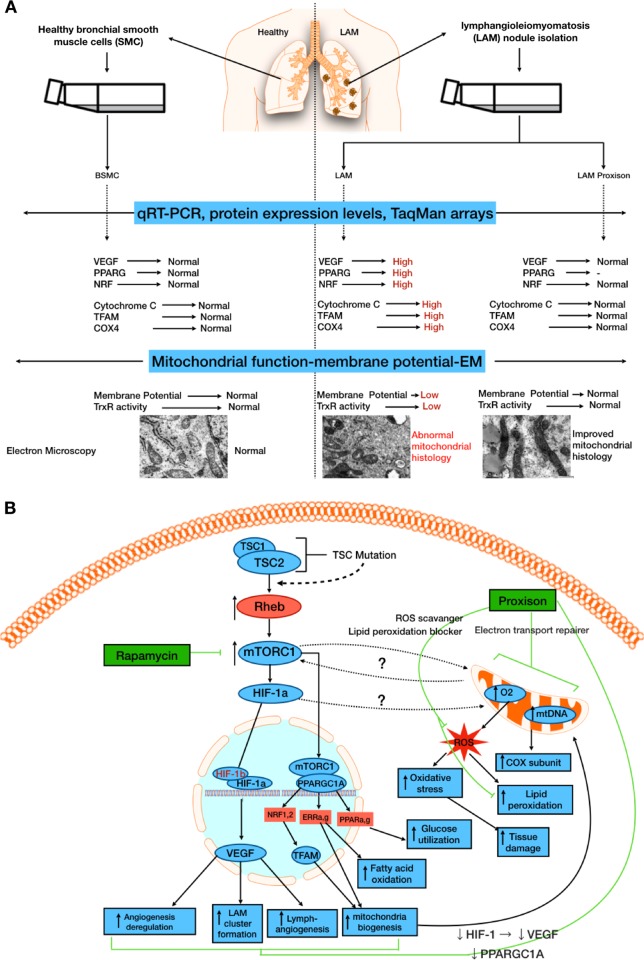
Fig. 4.
a Summary of LAM pathomechanism. b Summary of signaling pathway interactions in LAM revealing current and future therapeutic targets. The study led to the identification of mitochondrial dysfunction in LAM. Treatment with the mito-active candidate drug Proxison encouraged reestablishing the homeostasis in a diverse range of key pathways including VEGF and TFAM. Rapamycin, by acting directly on mTORC1, may also indirectly affect mitochondrial metabolism (as well as VEGF and TFAM), while Proxison, acting directly on the mitochondria, may indirectly influence the mTORC1 pathway. In migration assays the effects of the two drugs, Rapamycin and Proxison, were additive, indicating that from a clinical perspective there is a possibility of a combination therapy aimed at two different, but interacting facets of the disease process providing the best outcome for patients