Extended Data Figure 1. GC protection assays.
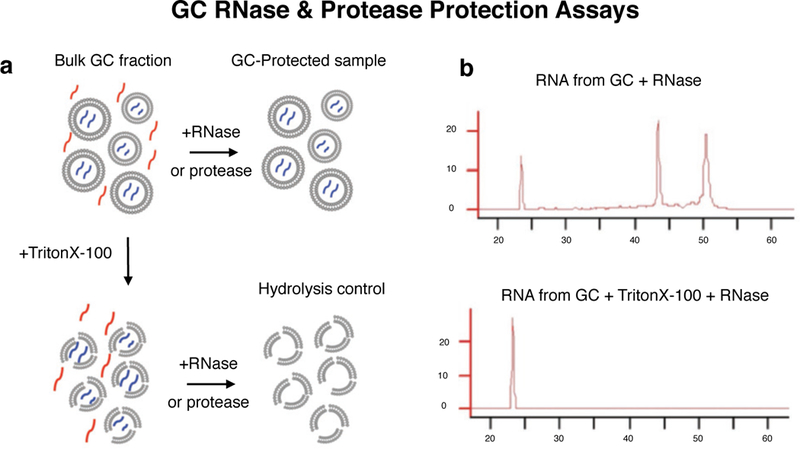
a, GC protection assay schematic: bulk GC fraction after subcellular fractionation is a suspension of GC particles enclosing GC-specific molecules (blue) within a medium that contains dilute soluble cytosolic molecules (red) from the homogenization process. Treatment with RNase or protease leads to hydrolysis of RNA and protein in the suspension medium that are not protected within GC particles, leaving only the GC-protected molecules (blue) in the sample. Addition of detergent (Triton X-100) prior to treatment results in hydrolysis of both cytosolic as well as GC-specific molecules due to ruptures in the encapsulating GC plasma membrane, providing a positive control for the efficiency of enzymes. The difference in RNA or protein signal between GC-protected and Hydrolysis control samples corresponds to the GC-specific signal. b, Bioanalyzer profiles show GC-protected RNA compared to detergent-treated control, with characteristic peaks corresponding to 28S and 18S rRNA, and a spectrum of low intensity signal characteristic of mRNA.
