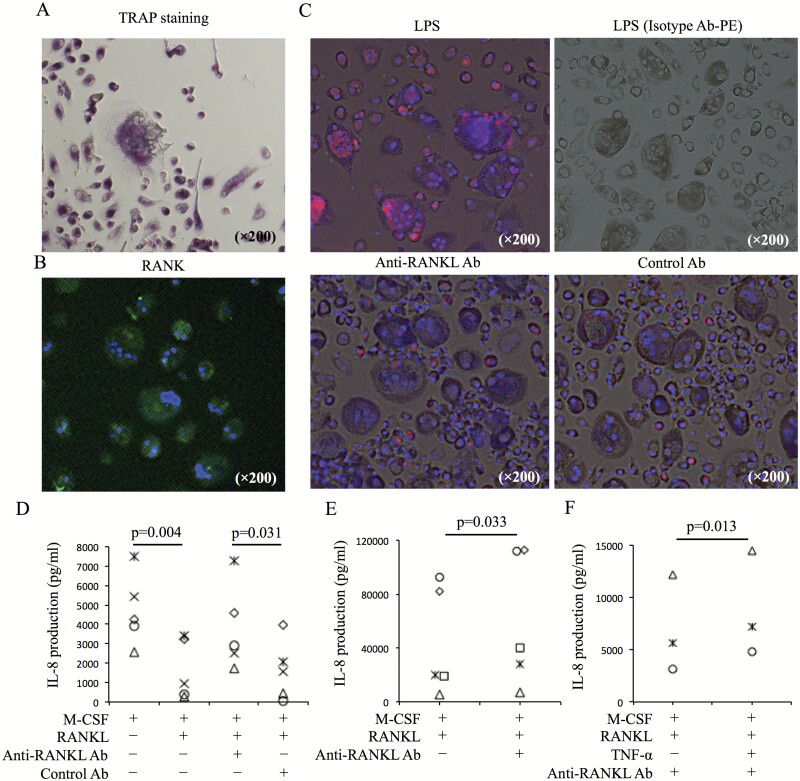
Fig. 2.
IL-8 production in OCL cultures induced from peripheral monocytes. (A) CD14+ cells from PBMCs of healthy donors were cultured with M-CSF (50 ng ml−1) and RANKL (125 ng ml−1). Ten days after culture, TRAP staining was performed. (B) Expression of RANKL in culture cells was evaluated by immunofluorescence staining (RANK-AF488 and DAPI). (C) IL-8 production in culture cells containing OCLs and pre-OCLs after LPS (1 ng ml−1) stimulation, anti-RANKL Ab (5 µg ml−1) treatment and control Ab (5 µg ml−1) treatment was evaluated by immunofluorescence staining (IL-8-PE, isotype control Ab-PE). (D) Ten days after culture of CD14+ cells with M-CSF and RANKL, the medium was changed, and cultured cells were incubated overnight in the following conditions: M-CSF only, M-CSF and RANKL, M-CSF and RANKL with anti-RANKL Ab (5 µg ml−1), and M-CSF and RANKL with control Ab (5 µg ml−1). After incubation, IL-8 levels in culture supernatant were measured (n = 5). (E) Synovial cells were cultured with M-CSF and RANKL. Five days after culture, medium was changed. Culture cells were incubated overnight with or without anti-RANKL Ab. After incubation, IL-8 levels in culture supernatant were measured (n = 5). (F) IL-8 levels in the culture supernatant of OCLs with M-CSF and RANKL [with or without TNF-α (50 ng ml−1)] after anti-RANKL Ab treatment were evaluated (n = 3). Representative images (A–C) from five healthy donors are shown. Statistical significance was evaluated using paired Student’s t-test (C and D). aRANKL Ab, anti-RANKL antibody.