Figure 1.
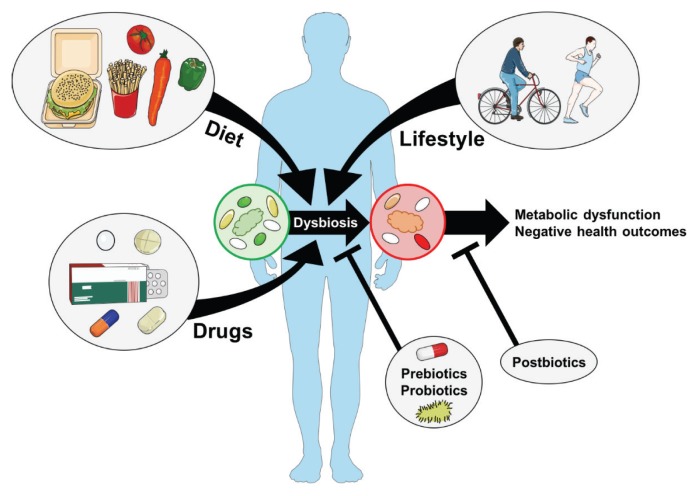
Environmental cues such as diet, drugs, and exercise combine to alter the composition of the gut microbiota. These and other external factors change the composition of the intestinal microbiota that can result in alterations to microbiota-derived compounds that influence host metabolism. For example, intestinal dysbiosis during obesity can modify the host’s ability to harvest energy from food, as well as susceptibility to metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The premise of prebiotics and probiotics is to restore or change the composition of the microbiota. However, another approach is to identify and use specific bacterial components or secreted factors of the microbiota that are known to have beneficial metabolic effects on the host (e.g. postbiotics). Postbiotics provide a unique alternative to mitigate metabolic disease factors without the need to alter the composition of the microbiota.