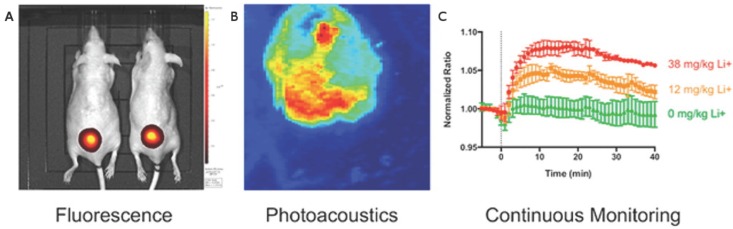
Figure 6.
Photoacoustic and fluorescent monitoring of systemic lithium concentration in vivo using injected bimodal nanosensors. (A) NIR fluorescence was used to image lithium concentration at the site of subcutaneous nanosensors administration. (B) Photoacoustic tomography shows the boundary of the subcutaneous nanosensor injection. (C) Photoacoustics and fluorescence were both used to measure nanosensor activation. Dose-dependent curves show continuous monitoring demonstrating that higher lithium concentrations yielded stronger signal. This also revealed that peak lithium was achieved at 18 min. Adapted with permission from 127, copyright 2015 American Chemical Society.