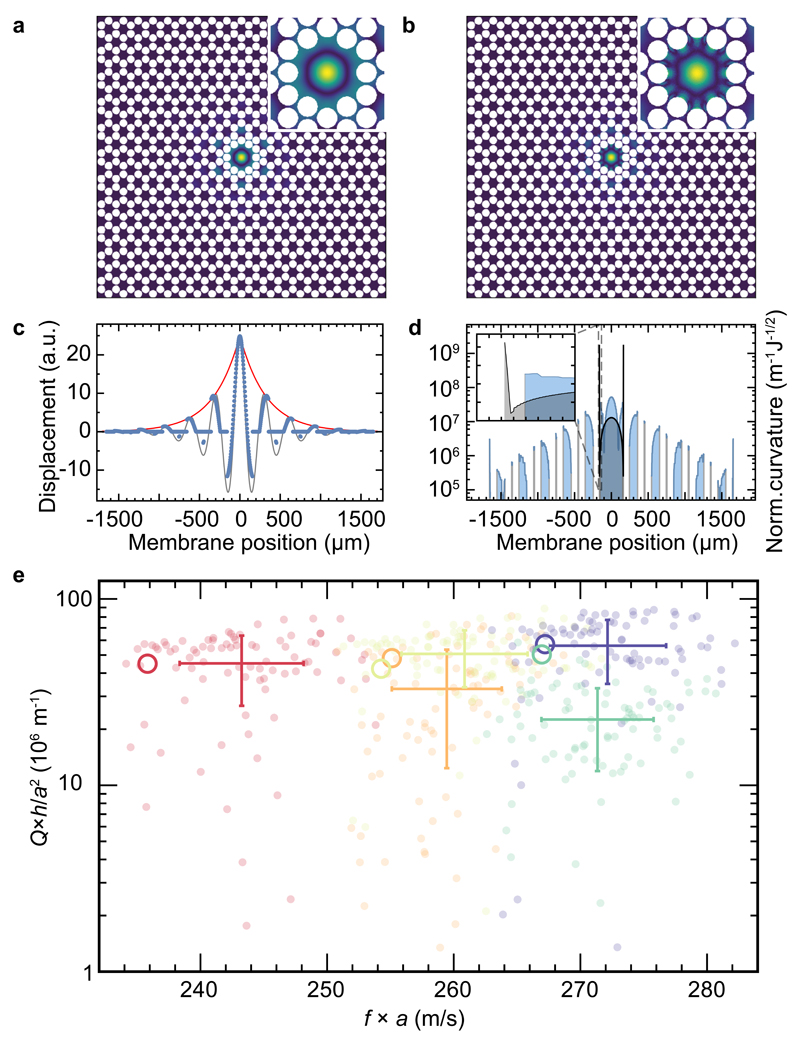
Fig. 4. Enhancing dissipation dilution.
a) Simulated displacement field of the fundamental defect modes and zoom on the defect (inset). b) Absolute value of mode curvature and zoom on the defect (inset). c) Simulated displacement along a vertical line through the defect (blue points). The red curve is an exponential function as a guide to the eye, while the grey curve represents a simplistic model of an exponentially decaying sinusoid (see text). d) Absolute value of mode curvature (blue line) along the same section as c). Curvature is normalised to the square-root of the total stored energy in the resonator. Also shown, for comparison, is the normalised curvature of a square membrane with the same frequency (grey line). Inset is a zoom on the membrane clamp, revealing the exceedingly large curvature of a rigidly clamped membrane, which is absent with soft clamping. e) Compilation of measured (transparent markers and errorbars, indicating standard deviations) and simulated (hollow circles) quality factors, normalised to a2/h, consistent with the observed scaling with the corresponding quantities for h = {35 nm, 66 nm, 121 nm}.