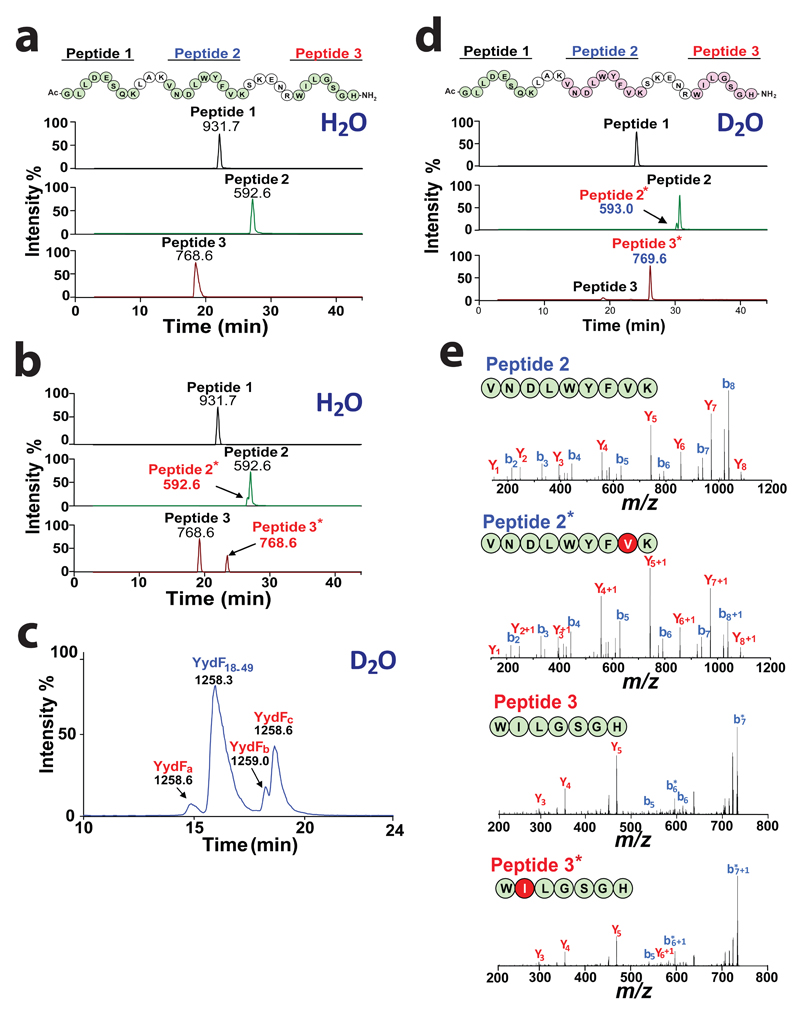
Figure 2. YydG catalyzes H-atom transfer to the peptide backbone.
Tryptic peptide mapping and LC-MS analysis of (a) YydF18-49 or (b) YydF18-49 after incubation with YydG. Numbers indicate the m/z value for each peptide. Sequences in green indicate the relevant peptide identified by LC-MS (i.e. Peptide 1: Ac-GLLDESQK, [M+H]+ = 931.7 ; Peptide 2: VNDLWYFVK [M+2H]2+ =592.6 and Peptide 3: WILGSGH-NH2, [M+H]+ =768.6). Sequences in pink represent the peptides modified by YydG. (c) LC-MS analysis of the peptide YydF18-49 after incubation with YydG in deuterated buffer. (d) Tryptic peptide mapping and LC-MS analysis of YydF18-49 after incubation with YydG in deuterated buffer. (e) LC-MS/MS analysis of Peptide 2 (upper left panel), Peptide 2* (lower left panel), Peptide 3 (upper right panel) and Peptide 3* (lower right panel) obtained after tryptic hydrolysis of YydF18-49 incubated with YydG in deuterated buffer (see full assignment in Supplementary Table S2-5).