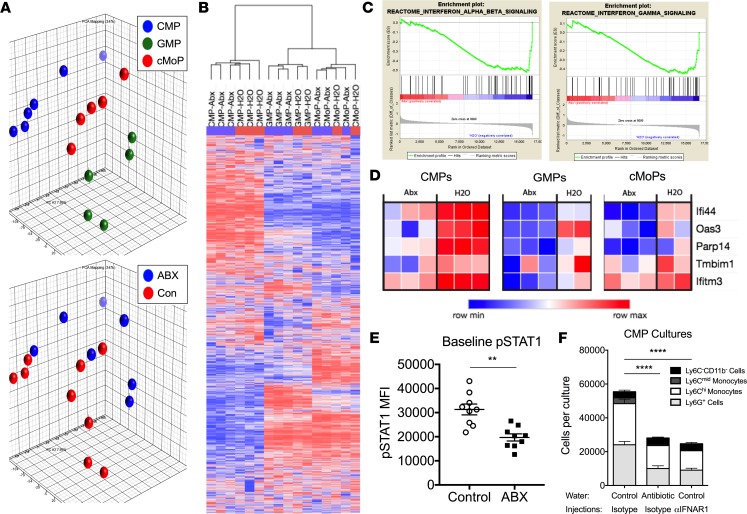
Figure 7. JAK signaling is altered in myeloid progenitors from antibiotic-treated mice.
(A–D) C57BL/6 mice were treated with antibiotic (ABX) or control water for 3 weeks prior to sacrifice and extraction of whole bone marrow cells. Bone marrow CMPs, GMPs, and cMoPs were sorted to isolate RNA for microarray analysis. (A) Principle component analysis was used to visualize the variance between samples in a 3-dimensional PCA plot. (B) Unsupervised hierarchical clustering analysis was used to compare the transcriptomes of each sample of the microarray. (C) Gene set enrichment analysis plots demonstrate negative enrichment of type I (left) and type II (right) IFNs genes in CMPs from antibiotic-treated mice. (D) Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) of differentially expressed genes identified suppression of IRF7 as an upstream regulator of the transcriptional changes observed between myeloid progenitors from antibiotic-treated and control mice. Heatmaps of the 5 IRF7-regulated genes identified by IPA analysis from the microarray data set are displayed. (E) Whole bone marrow cells were isolated from mice treated with antibiotic or control water for 3 weeks. Baseline levels of pSTAT1 in myeloid progenitors were measured by flow cytometry. Data were compiled from 2 separate experiments, for a total of 9 mice per group, and analyzed by a Mann-Whitney U test. (F) CMPs were sorted from mice treated with antibiotic or control water in combination with every-other-day dosing of an isotype antibody or anti-mouse IFNAR1 antibody for 3 weeks (n = 4 mice/group). Sorted CMPs were cultured for 7 days in media containing M-CSF, GM-CSF, IL-3, and SCF before enumeration of mature myeloid cell progeny by flow cytometry. Data were analyzed by 2-way ANOVA (***P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001, antibiotic-treated vs. control mice and antibiotic-treated vs. anti-IFNAR–treated mice).