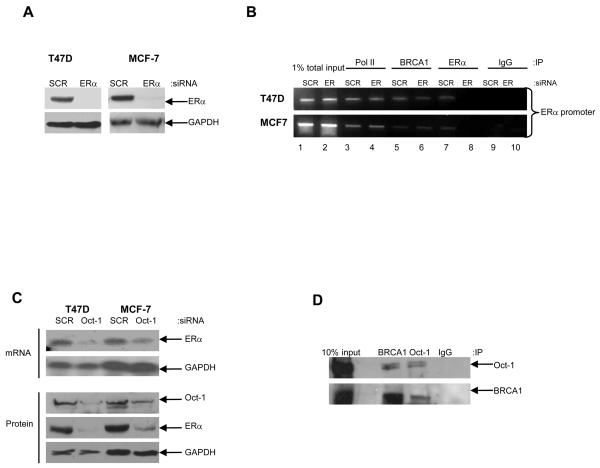
Fig. 4. BRCA1 mediated transactivation of ERα requires Oct-1 but not ERα.
A) Western blot analysis demonstrating efficient siRNA-mediated inhibition of endogenous ERα in comparison to scrambled control oligo (SCR). Equal loading was confirmed by reprobing with GAPDH antibody. B) ChIP analysis, using primers specific to the ERα promoter, shows recruitment of RNA Polymerase II (Pol II), BRCA1 and ERα to the ERα promoter in T47D and MCF-7 cells. ERα is recruited to the ERα promoter in the scrambled control cells (SCR) (Lane 7) but absent with siRNA-mediated inhibition of endogenous ERα (Lane 8). BRCA1 is present on the ERα promoter in both the scrambled control cells (Lane 5) and with siRNA-mediated depletion of endogenous ERα (Lane 6). 1% of total input DNA was used as a loading control (lanes 1 and 2). RNA Pol II and isotype matched IgG were used as positive and negative controls respectively (lanes 3, 4, 9 and 10). C) Reduction of Oct-1 protein levels by siRNA reduces ERα mRNA and protein in T47D and MCF-7 cells. Cells were transfected with either a scrambled control oligo (SCR) or Oct-1 specific siRNA oligo. Reprobing for GAPDH confirmed equal loading. D) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis showing association of endogenous BRCA1 and Oct-1 in T47D cells. 1mg of protein lysate was immunoprecipitated with BRCA1 antibody or Oct-1 antibody and immunoblotted for Oct-1 (top panel) or BRCA1 (bottom panel). 10% input lysate was loaded as a positive control. IgG was used as a negative control for immunoprecipitation.