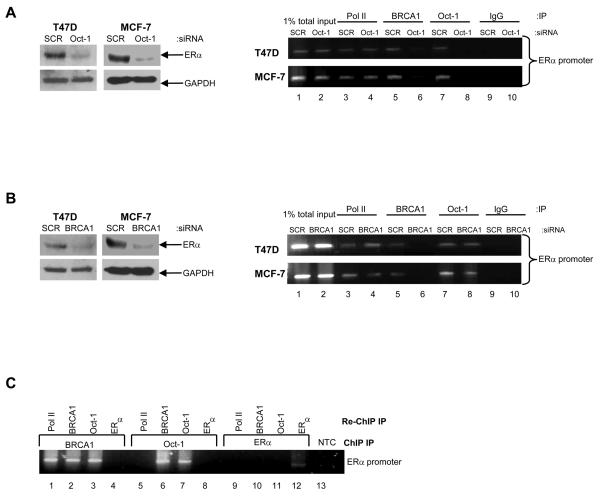
Fig. 5. Oct-1 recruits BRCA1 to the ERα promoter.
A) Western blot analysis confirming reduction of ERα protein expression with siRNA-mediated inhibition of endogenous Oct-1 in T47D and MCF-7 cells. From the identical experiment ChIP analysis shows recruitment of RNA Pol II, BRCA1 and Oct-1 to the ERα promoter in T47D cells. BRCA1 recruitment to the ERα promoter is impaired following siRNA-mediated depletion of endogenous Oct-1 (lane 6). 1% of total input DNA was used as a loading control (lanes 1 and 2). RNA Pol II and isotype matched IgG were used as a positive and negative controls respectively (lanes 3, 4, 9 and 10). B) Western blot analysis confirming the effect of siRNA-mediated inhibition of endogenous BRCA1 on ERα protein expression in T47D and MCF-7 cells. From the identical experiment, ChIP analysis demonstrates that recruitment of Oct-1 to the ERα promoter is independent of functional BRCA1 (lanes 7 and 8). 1% of total input DNA was used as a loading control (lanes 1 and 2). RNA Pol II and isotype matched IgG were used as a positive and negative controls respectively (lanes 3, 4, 9 and 10). C) Re-ChIP screening for interactions between factors recruited to the ERα promoter. Chromatin prepared from T47D cells was subjected to ChIP protocol, using antibodies for BRCA1 (lanes 1-4), Oct-1 (lanes 5-8) and ERα (lanes 9-12). Samples were then re-immunoprecipitated with antibodies for RNA Pol II, BRCA1, Oct-1 and ERα, respectively. NTC: no template control.