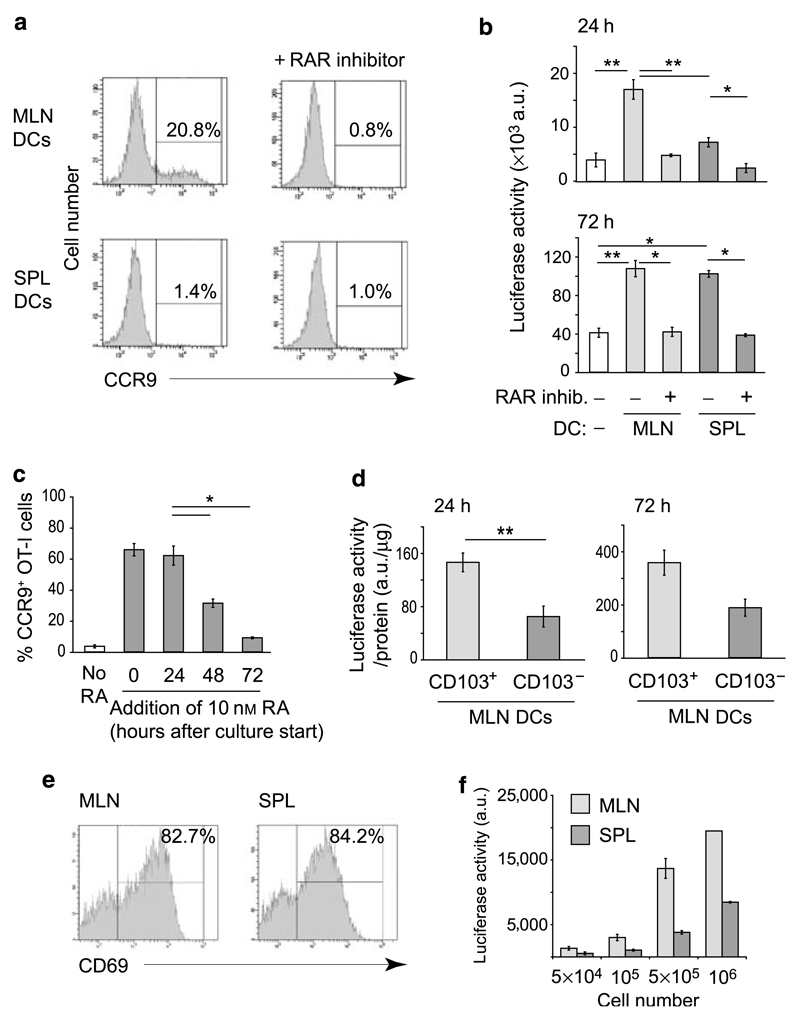
Figure 2. CD103+ MLN but not CD103− MLN or splenic DCs provide early RAR-stimulating signals required for efficient CCR9 induction.
(a) CCR9 expression by CD8+ T cells stimulated with anti-CD3 antibody in the presence of MLN or splenic DCs. A total of 2×105 DR5.CD8 cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 antibody (10 µg ml−1) in the presence of 105 MLN or splenic DCs, with or without the pan-RAR inhibitor AGN194310 (100 nM). Expression of CCR9 was determined by flow cytometry after 96 h. Numbers represent percentage of CCR9+ CD8+ T cells. (b) Luciferase activity of DR5.CD8 cells stimulated with anti-CD3 antibody in the presence or absence of MLN or splenic DCs. DR5.CD8 cells were cultured as in a. Luciferase activity was measured after 24 h (upper panel) or 72 h (lower panel). Bars represent mean±s.e.m. from four to six culture wells from two to three experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (c) Early RAR signaling is required for efficient CCR9 induction in responding T cells. CD8+ T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 antibody (10 µg ml−1). RA (10 nM) was added at indicated time points, and T-cell expression of CCR9 determined after 96 h of culture. Bars represent mean±s.e.m. of the percentages CCR9+ OT-I cells from four individual wells from two experiments. *P < 0.05. (d) Luciferase activity of anti-CD3 antibody (10 µg ml−1)-stimulated DR5.CD8 cells cultured in the presence of 105 CD103+ or CD103− MLN DCs isolated from Flt3L-treated mice. Luciferase activity was measured after 24 and 72 h and was normalized to the protein content of each individual well. Bars represent mean±s.e.m. from five to eight wells from two experiments. **P < 0.01. (e and f) Luciferase activity of in vivo-activated CD8+ T cells. DR5.OT-I mice were injected with OVA (200 µg, IP). Forty-two hours later, CD8+ T cells were purified from the spleen and MLN by MACS and analyzed for (e) CD69 expression by flow cytometry and (f) luciferase activity. (e) Numbers represent percentage of positive cells. (f) Bars represent mean±s.d. of three wells. CCR, CC chemokine receptor; DC, dendritic cell; IP, intraperitoneally; MACS, magnetic cell sorting; MLN, mesenteric lymph node; OVA, ovalbumin; RA, retinoic acid; RAR, retinoic acid receptor; SPL, splenic.