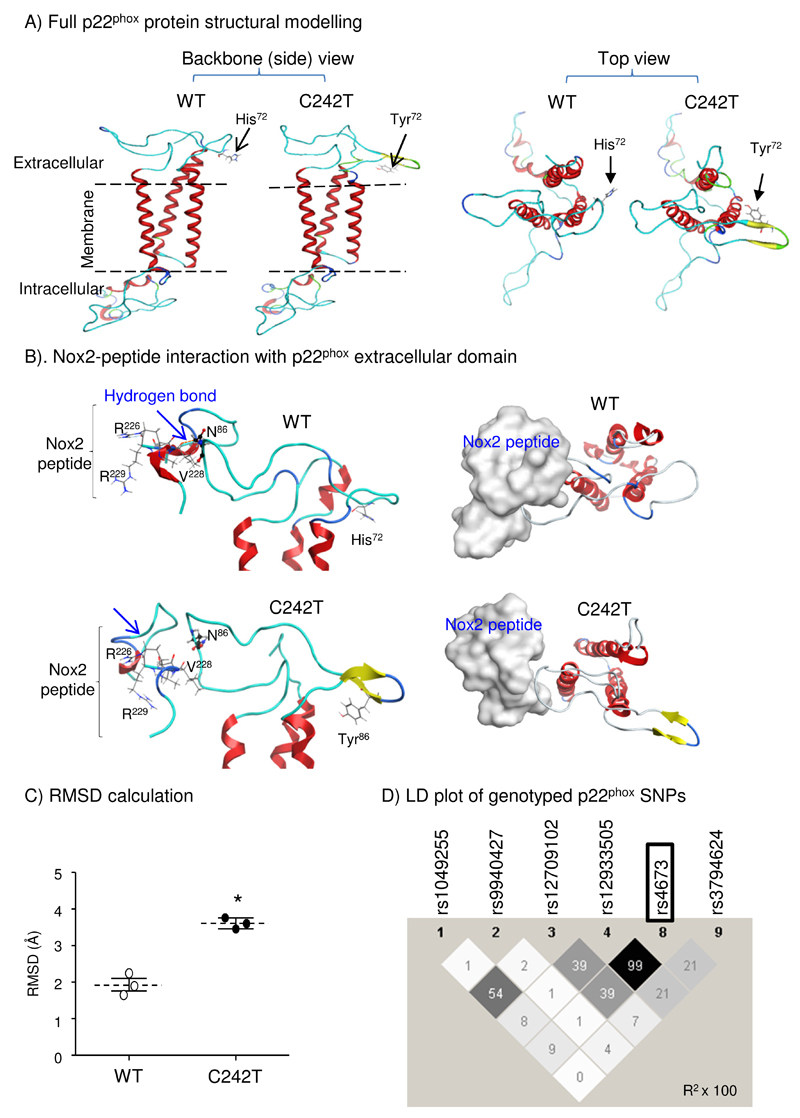
Figure 1. Computer modelling of p22phox structural changes associated with C242T SNP.
(A) Morphological differences between WT and C242T p22phox structures (ribbon presentation). (B) Docking of a Nox2-peptide (222-HGAERIVR-229) (skeleton in left panels and silver-space-fill in right panels) with p22phox extracellular domain (ribbon). Nox2 peptide interacts and forms an H-bond with the N86 (ball and stick presentation) of WT p22phox but not with the N86 of C242T p22phox. (C) RMSD calculations of the extracellular domain structural differences between WT and C242T p22phox following energy minimization. n=3 independent investigators. *p<0.05 for C242T values versus WT values (Mann-Whitney U-test). (D) Linkage disequilibrium (LD) plot from Haplo-view of common genotyped SNPs within the CYBA (p22phox) gene. The darker a diamond appears, the greater the correlation (r2 × 100) between the respective genotyped CYBA polymorphisms. The C242T SNP (rs4673) is outlined.