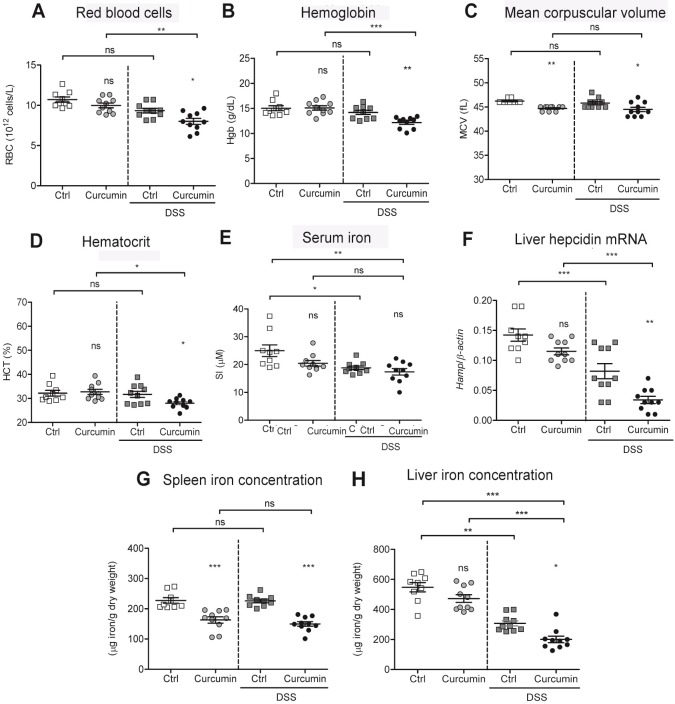
Fig 1. Curcumin supplementation of an iron-sufficient diet causes mild anemia in a DSS-mouse model.
C57BL/6 mice were fed an iron-sufficient diet (50 mg/kg chow; Ctrl) or an iron-sufficient diet supplemented with 2% curcumin (Curcumin). For dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) treatment, mice were fed an iron-sufficient diet with or without curcumin, starting 2 weeks before administration of DSS. (A-D) Erythroid parameters: red blood cells, hemoglobin, mean corpuscular volume, and hematocrit. (E) Serum iron levels. (F) Liver hepcidin (Hamp) mRNA expression against housekeeping β-actin mRNA. (G-H) Iron content in spleen (G) and liver (H). Results are representative of a minimum of three independent experiments; n = 9–10 mice per group. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ns = not significant between Curcumin to Ctrl groups and when indicated between non-DSS and DSS groups.