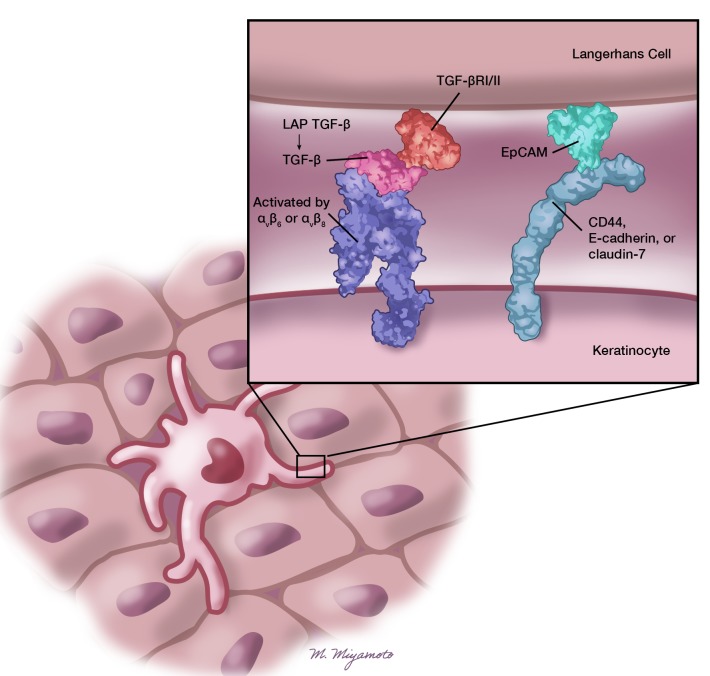
Figure 1. Langerhans cells interact with keratinocytes in the epidermis through multiple junctions.
In the steady state, the retention of Langerhans cells in the epidermis requires the conversion of TGF-β bound to the latency-associated peptide (LAP) to active TGF-β by integrins αvβ6 or αvβ8 expressed on the keratinocyte surface. Interactions between the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) on Langerhans cells and claudin-7, a variant of CD44, or epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin) expressed on keratinocytes may regulate Langerhans cell migration. DLN: draining lymph node. Illustrated by Mao Miyamoto.