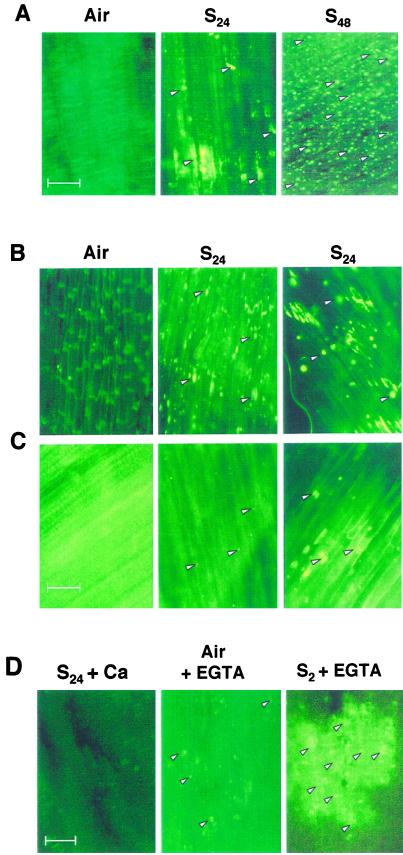
Figure 7.
Fluorescence detection of callose within the 15-mm tip of maize roots. A, Non-mutant seedlings were incubated aerobically (Air) or submerged for 24 (S24) or 48 h (S48), fixed, and stained in aniline blue. Bright fluorescence spots (a few indicated by arrowheads) represent callose deposits. B and C, Callose development in the root tip of sus1 and sh1 mutant maize seedlings, respectively. Subpanel designations are as in A. Right and middle, S24 is from proximal (within 0.5 cm of the root apex) and distal regions of the root tip (the region above 0.5 cm of the root apex), respectively. In these genotypes there was a clear distinction in the staining of these two zones. D, Effect of EGTA and Ca2+ supplementation on callose development in non-mutant seedlings. S24+Ca, Seedlings submerged for 24 h in the presence of 2 mm CaCl2; Air + EGTA, seedlings incubated aerobically in 2 mm EGTA; S2+EGTA, seedlings submerged for 2 h in the presence of 2 mm EGTA. The glare in some control panels is due to light intensity adjustment to compensate the dark background caused by a lack of specific aniline blue staining. Scale bars = 50 μm.