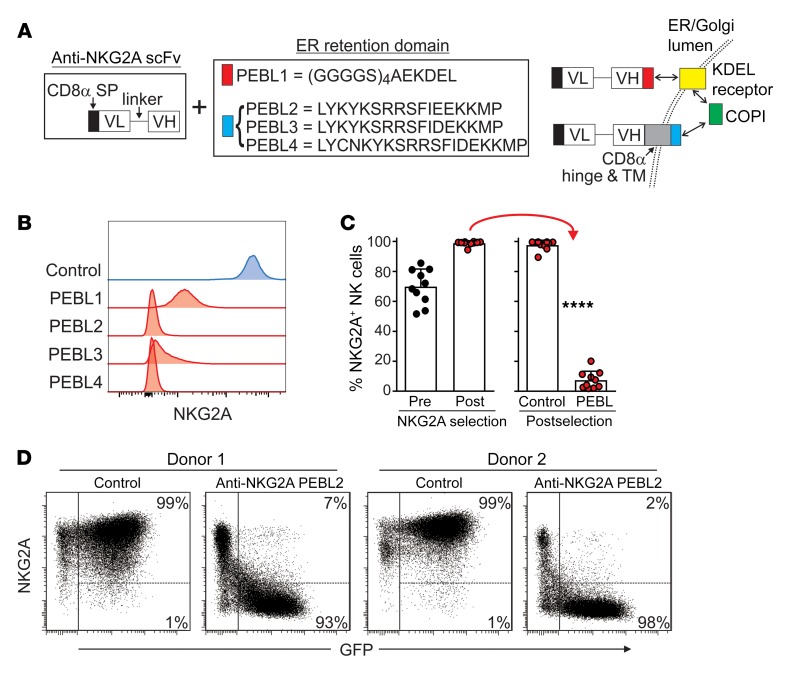
Figure 2. Downregulation of NKG2A expression in NK cells with anti-NKG2A PEBLs.
(A) Schematic representation of the anti-NKG2A PEBL constructs and their mechanisms of action. The PEBL constructs consist of a CD8α signal peptide and an anti-NKG2A scFv followed, at the C terminus, by the sequences listed in the box, according to each PEBL. PEBL1 binds to the KDEL receptor, which joins the COPI. PEBLs 2–4 bind directly to COPI. VL, light chain variable domain; VH, heavy chain variable domain. (B) Downregulation of NKG2A expression in NK92 cells. Flow cytometric histograms show surface expression of NKG2A, as detected by anti-NKG2A APC (Miltenyi Biotech), after transduction with a vector containing GFP only (Control) or GFP plus PEBLs 1–4. (C) NKG2A+ expanded human NK cells were purified by magnetic bead–positive selection and transduced with anti–NKG2A-PEBL2 or with GFP only. Shown are the percentages of NKG2A+ cells before and after purification and after transduction (10 experiments with NK cells from 9 donors), as measured by flow cytometry. ****P < 0.0001, t test. (D) Representative flow cytometry dot plots of 2 of the experiments shown in C. The right area in each dot plot encloses GFP+ (i.e., transduced) NK cells; the percentages of NKG2A+ and NKG2A cells among these cells are shown.