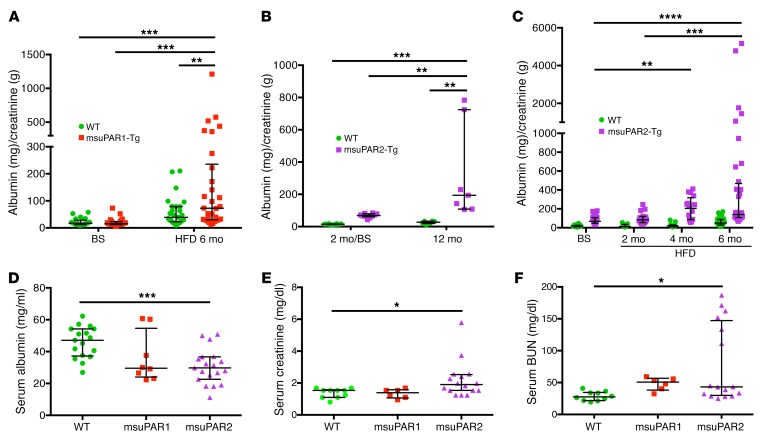
Figure 3. msuPAR2-Tg mice develop progressive proteinuria and severe kidney dysfunction.
(A) Proteinuria profiling in msuPAR1-Tg mice. Proteinuria, in terms of ACR, which was absent before HFD treatment at baseline, developed in msuPAR1-Tg mice after 6 months of HFD. n = 25 WT/baseline (BS); n = 26 msuPAR1-Tg/BS; n = 27 WT/HFD6mo; n = 30 msuPAR1-Tg/HFD6mo. Two-way ANOVA; data were log-transformed to normal distribution. (B) Spontaneous proteinuria in msuPAR2-Tg mice. Without HFD treatment, proteinuria was evident in msuPAR2-Tg mice at 2 months of age and increased significantly by 12 months of age. n = 9 at 2 mo (2 month) /BS; n = 7 at 12 mo. Two-way ANOVA. (C) With HFD treatment, msuPAR2-Tg mice developed accelerated and progressive proteinuria over a period of 6 months. n = 30 WT/BS; n = 26 msuPAR2-Tg/BS; n = 9 WT/HFD2mo; n = 16 msuPAR2-Tg/HFD2mo; n = 13 WT/HFD4mo; n = 16 msuPAR2-Tg/HFD4mo; n = 31 WT/HFD6mo; n = 36 msuPAR-Tg/HFD6mo. Baseline was at 2 months old, before HFD treatment. Two-way ANOVA. Data were log-transformed to normal distribution. (D) Serum albumin decreased significantly in HFD-treated msuPAR2-Tg mice compared with WT (littermate control) mice. n = 17 WT; n = 8 msuPAR1-Tg; n = 19 msuPAR2-Tg mice. One-way ANOVA. (E) Serum creatinine increased significantly in HFD-treated msuPAR2-Tg mice. n = 10 WT; n = 6 msuPAR1-Tg; n = 16 msuPAR2-Tg mice. One-way ANOVA. (F) Serum BUN levels increased significantly in HFD-treated msuPAR2-Tg mice. n = 10 WT; n = 6 msuPAR1-Tg; n = 16 msuPAR2-Tg mice. One-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.