Fig. 4: OPC perivascular clusters disrupt the BBB.
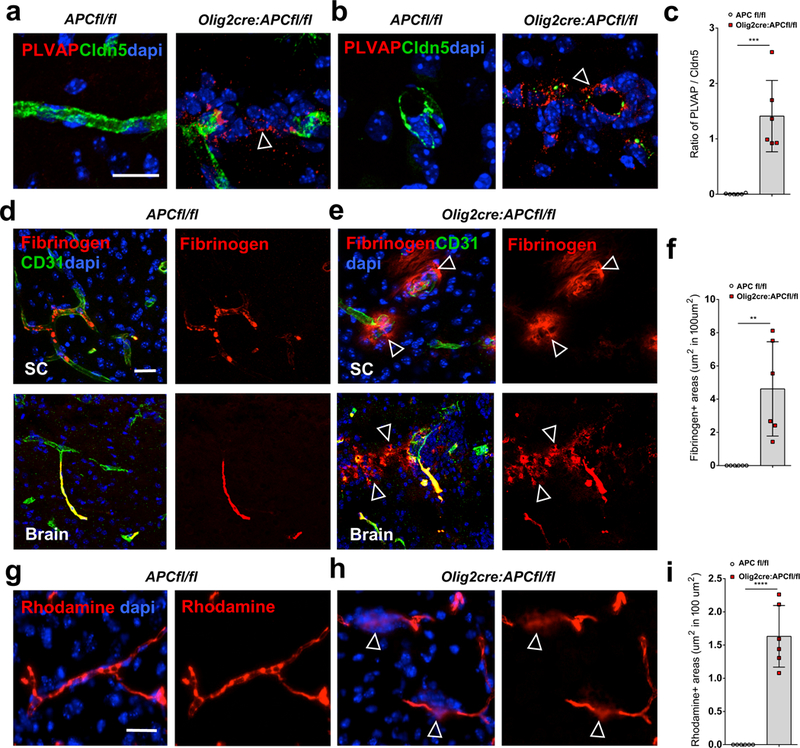
(a-b) Staining for plasmalemma vesicle-associated protein (PLVAP) and claudin5 (Cldn5) in P9 spinal cord of Olig2-cre:APC fl/fl and APCfl/fl control mice around vessels in longitudinal (a) and transverse (b) views. A PLVAP+/claudin5- state around OPC clusters in Olig2-cre: APC fl/fl mice (arrows) identifies areas of immature BBB. (c) Ratio of PLVAP:Cldn5 expression on endothelium in areas with OPC perivascular clusters in Olig2-cre:APC fl/fl spinal cord compared to comparable regions without clusters in APCfl/fl controls (n=6 animals, p=3.29 E-4). Data were analyzed by unpaired two-sided Student’s t test. (d-e) Staining shows fibrinogen only within the lumen of CD31+ blood vessels in P9 APCfl/fl control spinal cord (SC) and brain (d), but leaking into parenchyma (arrows) around OPC clusters (stained with dapi) in Olig2-cre:APC fl/fl (e). (f) Quantification of area of fibrinogen staining outside blood vessels in CNS parenchyma per mm2 in SC of Olig2-cre:APC fl/fl and APCfl/fl controls (n=6 animals, p=0.0026). Data were analyzed by unpaired two-sided Student’s t test. (g-h) Dextran- tetramethylrhodamine (rhodamine) injection into P9 Olig2-cre:APC fl/fl tail vein (h) shows extravasation into brain parenchyma (arrows in h) around OPC perivascular clusters (stained with dapi), which is not seen in APCfl/fl control mice (g). (i) Quantification of area of rhodamine staining outside blood vessels in CNS parenchyma per mm2 in SC of Olig2-cre:APC fl/fl and APCfl/fl controls (n=6 animals, p=6.46 E-6). Data were analyzed by unpaired two-sided Student’s t test. Scale bars, 20μm in all panels. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001. Values are mean ± s.d.
