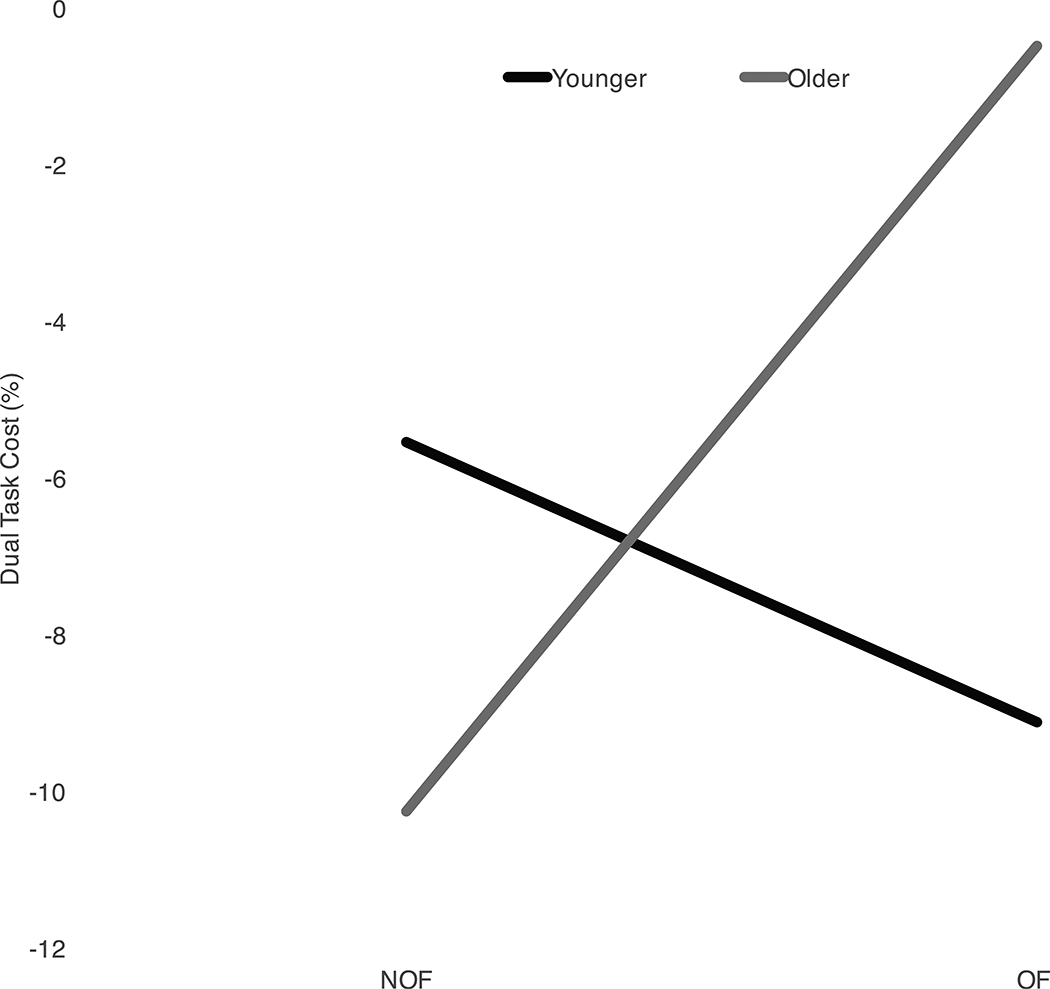
Fig 3.
The dual task cost (DTC) (−) and benefit (+) in no optic flow (NOF) (A) and optic flow (OF) (B) environments for step width (SW) and step length (SL) for all cognitive tasks compared to baseline walking for healthy young and older subjects. Younger adults had a greater DTC for step width as compared to older adults when performing serial subtractions in both NOF and OF (p=0.02). (C) During the letter fluency task, older adults demonstrated less cost whereas, the young adults demonstrated increased cost due to OF