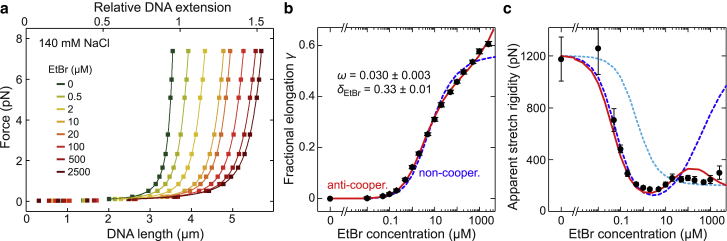
Figure 2.
DNA elongation and decreased stretch rigidity due to ethidium intercalation. (a) Force-extension curves (colored squares) recorded for EtBr concentrations from 0 to 500 μM in the presence of 140 mM NaCl. From fitting an extensible WLC model to the data (solid lines), the zero-force DNA contour length and the apparent stretch rigidity were obtained. (b) Fractional elongation of the DNA contour length at zero force as a function of the EtBr concentration (black circles) obtained from the force-extension data. Fits to the data using a noncooperative and an anticooperative binding model are shown as dashed blue and solid red lines, respectively. Best-fit parameters are given for the anticooperative model. (c) Apparent DNA stretch rigidity as function of the EtBr concentration (black circles) obtained from the force-extension data. Predictions from modeling force-induced intercalation using the noncooperative and the anticooperative binding model are shown as dashed blue and solid red lines, respectively. The prediction of a serial combination of rigid bare and soft ethidium-complexed DNA segments is shown as a dotted cyan line.