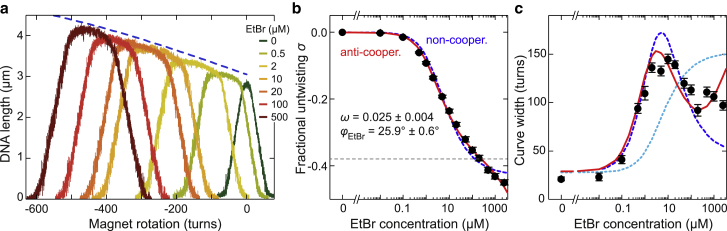
Figure 3.
DNA untwisting and torsional softening due to ethidium intercalation. (a) DNA supercoiling curves recorded for EtBr concentrations from 0 to 500 μM in the presence of 140 mM NaCl. DNA untwisting by the intercalation of ethidium shifts the curves to negative turns. The predicted DNA length at zero torque as function of the untwisting is shown as a blue dashed line (curve shifted to larger length for clarity). (b) Fractional untwisting of the DNA at zero torque as a function of the EtBr concentration (black circles) from the centers of the supercoiling curves. Fits to the data using a noncooperative and an anticooperative binding model are shown as dashed blue and solid red lines, respectively. Best-fit parameters are given for the anticooperative model. The expected untwisting for binding at every second basepair stack is shown as a gray dashed line. (c) Plateau width of the measured supercoiling curves as a function of the EtBr concentration (black circles). Predictions from modeling torque-induced intercalation using the noncooperative and the anticooperative binding model are shown as dashed blue and solid red lines, respectively. The prediction for a serial combination of torsionally rigid bare and soft ethidium-complexed DNA segments is shown as a dotted cyan line.