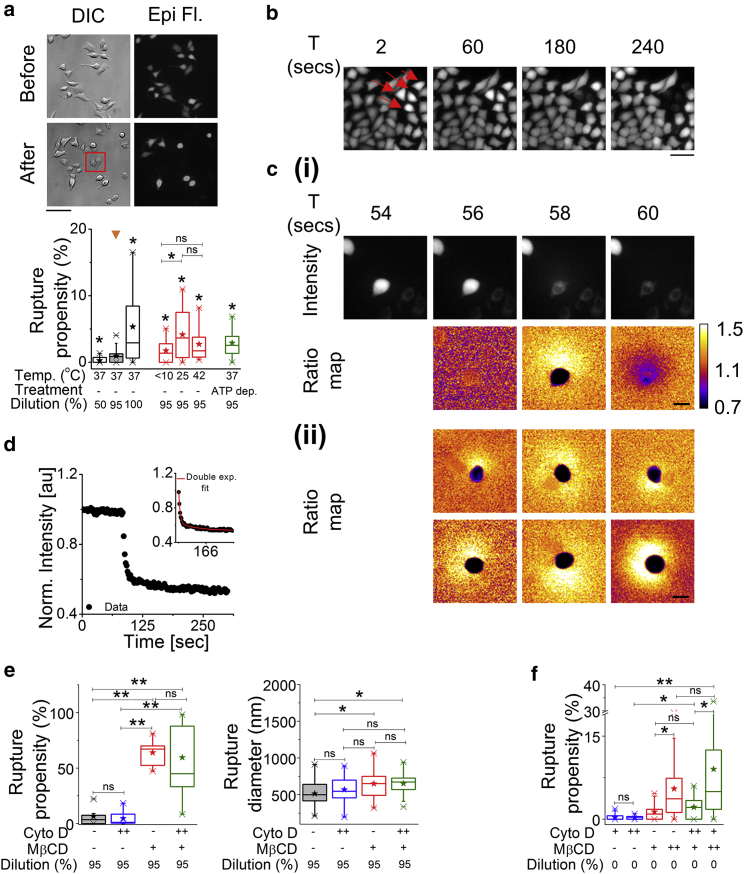
Figure 5.
Membrane rupture induced by hypo-osmotic/iso-osmotic medium in the presence of MβCD. (a) Top: shown are DIC and epifluorescent images of Calcein AM-labeled HeLa cells before and after the administration of a 95% hypo-osmotic shock (Scale bars, 100 μm). Among others, the cells in the box are representatives of membrane rupture. Bottom: shown is a box plot of rupture propensity of cells due to change in hypo-osmotic stress, change in temperature, and ATP depletion (N = 3 experiments each). (b) Top: shown are time lapse images of Calcein AM-loaded HeLa cells undergoing rupture (arrowheads in red) (Scale bars, 50 μm). (c) (i) Shown is the intensity and ratio map of a rupturing cell followed in time to show single point rupture. (ii) Shown are representative ratio maps of six different cells showing an asymmetric spread of fluorescence after rupture (Scale bars, 30 μm). (d) A time profile of normalized mean intensity of a ruptured cell is shown; inset shows the double exponential fit to the profile. (e) Shown are box plots of rupture propensity (left) and rupture diameter (right) of 95% hypo-osmotic shock administered HeLa cells under control, Cyto D (2 h post-treatment), MβCD (50 min post-treatment), and Cyto D + MβCD conditions (N = 3 experiments each). (f) Shown are box plots of rupture propensity of cells under Cyto D, MβCD, and dual drug treatments (N = at least three experiments each) in the absence of hypo-osmotic shock. “+” denotes 60 min treatment (for Cyto D) and 50 min (for MβCD), and “++” denotes 120 min treatment. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.001, ns p > 0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. See Fig. S7 and Table S3 for statistics. To see this figure in color, go online.